Cryptography Reference
In-Depth Information
Attacks are performed on two different setups: the publicly available power
curves of DPA Contest 2008/2009 [30] of a DES implementation and curves
acquired on an Atmel STK600 board with an Atmel AVR ATmega2561 [1] of a
multi-precision multiplication algorithm.
On DPA Contest 2008/2009 curves of a DES, the intermediate value targeted
is the output the SBox in the last round. For the attacks using mutual infor-
mation with nonparametric estimation, we consider no power model, i.e. the
value of the data. The Hamming weight model is used for the other attacks.
Each attack is performed on 135 sets of 600 power curves in order to average
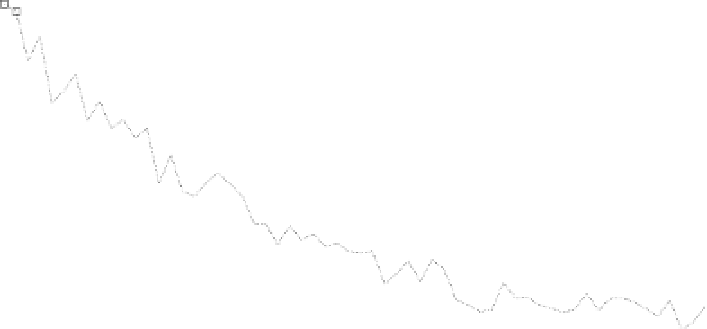
the results. We evaluate each distinguishers and present the results in Fig. 1.
Attacks can be assigned to different groups depending on their eciency. The
best seems to be CE, CPA and SPE which are all parametric tests. The fol-
lowing attacks are KDE, DCA and CVM amongst which are the first mutual
information nonparametric ones. The BSE is next, followed by KNN, GMIA and
HE.
40
CPA
CVM
GMIA
KDE
KNN
HE
BSE
CE
SPE
DCA
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
Number of curves
Fig. 1.
Guessed entropy results on DPA Contest 2008/2009 curves of a DES
The same attacks are also performed on curves acquired on a STK600 develop-
ment board with a 8-bit Atmel AVR ATmega2561. This setup is not particularly
well suited to perform side-channel attacks. Therefore the power traces contains
significantly more noise than the DPA Contest ones. We attack a column-wise
multi-precision multiplication algorithm implemented in software. The targeted
values are the intermediate 8-bit multiplications
x
i
×
y
j
considering one of the




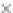
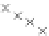
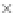
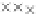
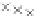
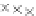
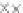


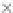
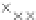
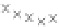
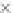
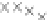
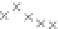

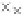

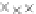

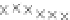
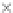




































































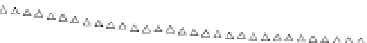








































































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search