Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
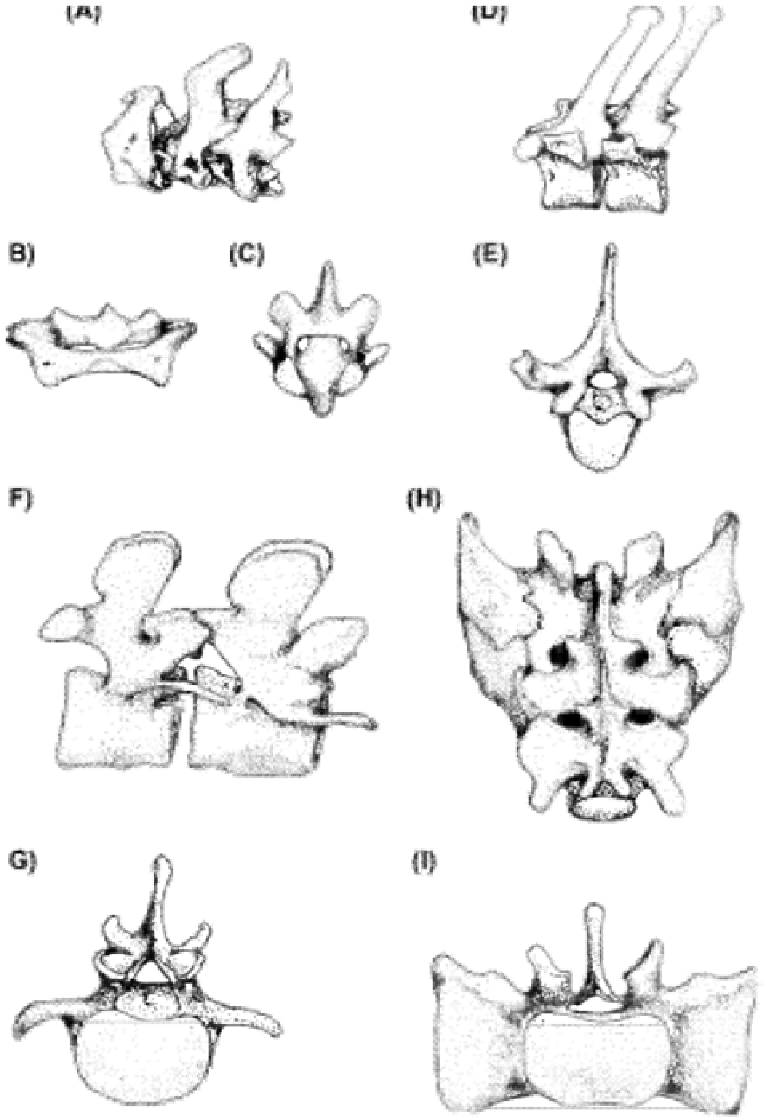
FIGURE 4.10
Regional differences between vertebrae (Macaca mulatta). (A
e
C) Cervical vertebrae: (A) lateral view C1 through C3; (B) posterior
view C1; (C) superior view C2. (D,E) Thoracic vertebrae: (D) lateral view T5 and T6; (E) superior view T6. (F,G) Lumbar vertebrae: (F) lateral view L4
and L5; (G) superior view L5. (H,I) Sacrum: (H) dorsal (posterior) view; (I) superior (cranial) view S1. Note that the important characteristics of each
region are shown here but that the vertebral column is a continuum and individual vertebrae vary depending on their relative position. The sizes and shapes
of the spines, articular facets, and bodies of one region blend with those of the adjacent region. (Drawings by Nancy Hong.)
the basic patterns described in topic on human anatomy.
One interesting difference, however, is the larger size of the
external carotid artery, which principally supplies the face,
in comparison with the internal carotid artery, the primary
Neurovascular Systems of Head and Neck
The vascular system in the head and neck of nonhuman
primates, including arteries, veins, and lymphatics, follows