Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
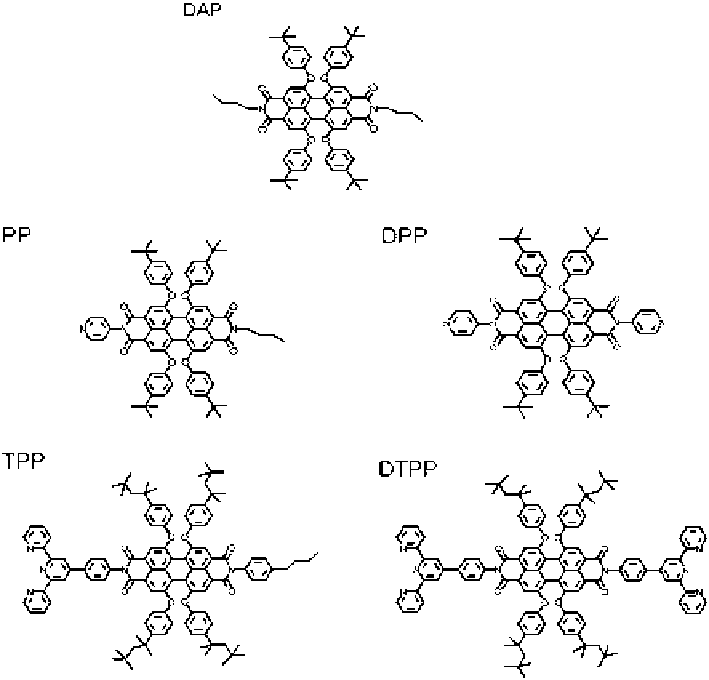
Fig. 4.3
Chemical structure and abbreviations for perylene diimides (PDI).
DAP
dialkyl-PDI,
PP
(pyridyl)
1
-PDI,
DPP
(pyridyl)
2
-PDI,
TPP
(ter-pyridyl)
1
-PDI,
DTPP
(ter-pyridyl)
2
-PDI
Like in the case of multiporphyrin complexes previously studied in our group
[
107
,
108
,
111
-
113
], the existence of substituted pyridyl rings in these organic
ligands offers the possibility for a controllable formation of “QD-Dye” nanoassem-
blies via a non-covalent coordination “key-hole” principle during titration experi-
ments in solution [
62
,
63
,
65
,
75
,
90
,
101
]. It is well known for chemical reasons
that the transition metal ions Zn
2
+
or Cd
2
+
have an empty 3d
10
orbital while
the heteroatom
N
-pyr of the porphyrin
meso
-pyridyl ring is a very good e-donor
having an electron lone pair orbital. Correspondingly, in this case a “key-hole”
principle is realized via one- or two-fold non-covalent coordination Zn
2
+
····
N
-pyr
or Cd
2
+
····
N
-pyr. Recent calculations with respect to the bonding conditions of
ligands [
106
] have shown that the bond strength for the ligands can be described in
most cases by electrostatic interactions between the partial charges of the respective