Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 1.10
m-wide GaAs channel.
(
c
) Optical image of the Metal-Semiconductor-Metal (MSM) diode. Adapted from [
17
]. Copyright
2011 American Physical Society
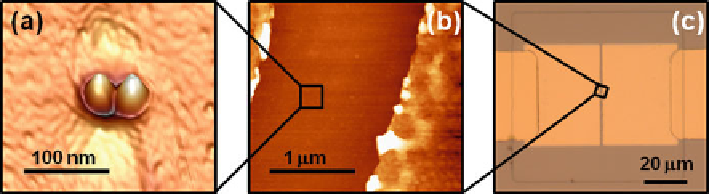
Topography AFM images of (
a
) a single QDM, and (
b
) a 1.5-
statistics of the neutral exciton under a lateral electric field [
16
]. However, the
observation of electrically tunable energy anticrossings in lateral QDMs remains a
difficult task, mainly due to the exponential decrease of the tunnel coupling energy
with the QD center-to-center distance [
6
,
16
,
49
]. In the following, we will show
the emission spectrum by micro-PL of electrically tunable lateral QDMs with a
varying number of electrons. Particularly, it is observed that for a QD center-to-
center distance of 30-40 nm electron tunneling affects the negative trion emission
energy in the molecule before clear exciton anticrossings may take place.
A typical lateral QDM used in this study shows a mean QDs center-to-center
separation of 37
4nm(Fig.
1.10
a). In order to apply an electric field along the
QDs pair mutual axis, a metal-semiconductor-metal (MSM) diode is defined by
evaporation of two metal contacts consisting of 15 nm Mo
±
+
30 nm Au on top of
100-
mwide
un-doped GaAs channel embedding the nanostructures, as shown in Fig.
1.10
a-c.
The micro-PL of individual QDMs is collected at 5 K using a fiber-based confocal
microscope excited with 785-nm continuous-wave laser light, dispersed by a
2m
m-square mesas. The contacts are separated by an 80
m long
×
1.5
0.3 m focal length double spectrograph and detected with a peltier cooled
silicon charge coupled device (CCD) camera.
The emission of single semiconductor nanostructures in the presence of a lateral
electric field has been studied in the last few years [
50
]. For moderate electric fields,
or when the separation between the contacts is large, the changes observed in the
QD emission spectrum have been related to the modulation of the carrier capture
probability induced by the external field. On the other hand, for large enough electric
fields or a small contact separation for a given lateral bias range, a modulation of the
electronic confinement levels can also be obtained. In this regime, the exciton wave
function can be directly modified, which leads to energy shifts, carrier tunneling, and
fine-structure splitting reduction, among other effects [
51
,
52
]. The MSM diodes
used in this study were designed to have a channel width of only 1.5
×
m, which
allows for applying large electric fields along the GaAs [1 1 0] crystallographic
direction (0-60 kV cm
−
1
). This is required to independently tune the exciton energy
of the two QDs in the lateral QDM and, if their center-to-center separation is small
enough, to observe resonant quantum tunneling phenomena [
6
,
16
,
53
].