Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
Herpes 8
Herpes 5
HIV 2
Herpes 4
Herpes 1
HIV 1
0.5
1
1.5
0.5
1.5
SIR
score
SIR
score
c
d
0.5
HBV A
HBV B
HBV C
HBV D
HBV E
HBV F
HBV G
HBV H
gsHBV
0.4
0.3
0.2
WHV
0.1
DHBV
gooseHBV
heronHBV
0
0.5
1
1.5
0.5
1
1.5
SIR
score
SIR
score
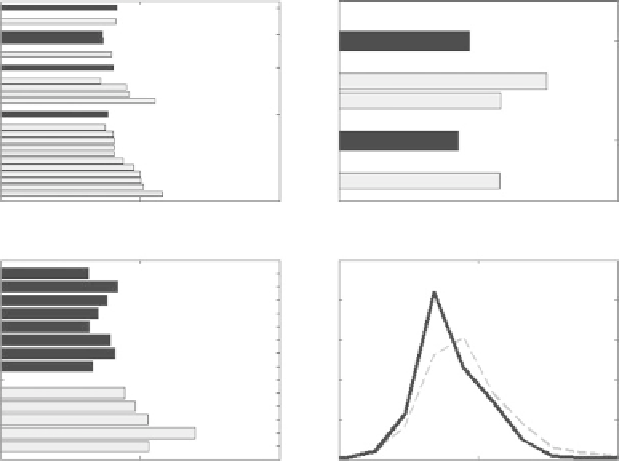
Fig. 3
The average SIR score of human vs. non human viruses. Data is shown for three viruses:
herpes virus (HHV-1, HHV-4, HHV-5 and HHV-8), HIV (HIV-1 and HIV-2) and Hepatitis B
(strains A-H) virus. The
black columns
represent human strains while the
grey columns
represent
non-human strains. In most cases the average SIR score of the human viruses is lower than the non
human viruses. The
lower right
drawing represents the SIR score distributions of all full sequenced
viruses from the NCBI. In general, the SIR score of the non-human viruses was distributed around
1 while the human virus was less than 1
classified into three major subfamilies and eight herpesviruses. They have been
identified as having humans as their primary host. With the exception of KSHV
and HSV2, the human herpesviruses are ubiquitous, and infections with these
viruses are common worldwide. The herpesvirus genome is 120-250 kbp encoding
dozens of genes and several microRNAs. Within all characterized herpesvirus
genomes there are conserved regions that mainly encode for structural proteins
and replication enzymes, and are more conserved between members of the same
subfamily than they are between subfamilies. Herpesviruses exhibit two divergent
phases of infection: lytic (productive) and latent (non-productive), characterized by
distinct patterns of viral gene expression.
Extensive viral gene expression characterizes productive infection which culmi-
nates in virus production and release along with cell lysis and death. In contrast,
only few viral genes are expressed and no viral progeny is produced during the
latent phase in which the virus genome is maintained as a circular episome in the
host cell. Several physiological conditions may induce reactivation of a hidden
virus, switching the latent infection into a lytic. In fact, primary host infection
Search WWH ::

Custom Search