Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
0
.
25 cm, the side-branch radius of 0
.
075 cm, and the aneurysm radius of 0
.
4cm.The
side-branch length is 1
.
2 cm. The idealized geometry volumetric mesh is composed
of approximately 0
.
5
M
tetrahedral elements, with elements of size 0
.
02 cm.
5
Discussion
5.1
Idealized Geometry
Hemodynamics inside the idealized aneurysm was studied using the Newtonian and
Carreau fluid models, both in steady and unsteady inflow regimes, including and
excluding a side-branch within the aneurysm, and prescribing four different types
of outflow boundary conditions on the side-branch: traction-free (TF), no-slip (NS),
3D-1D coupling (1D), and 3D-0D coupling (0D). At the outflow section of the
main vessel a traction-free boundary condition was always prescribed.
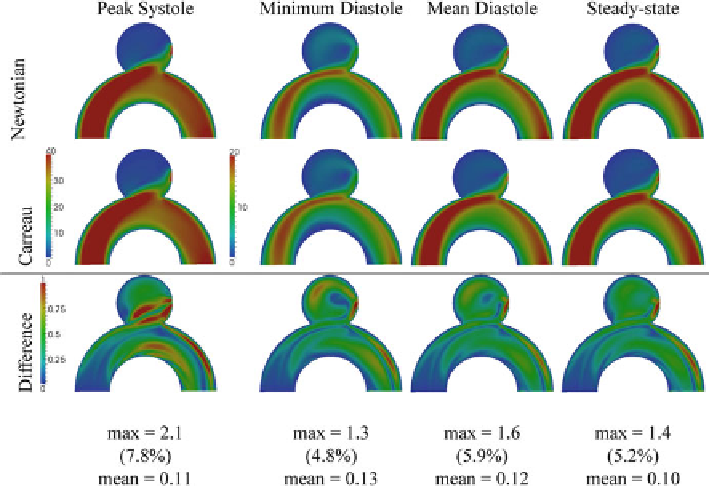
The differences between the Newtonian and Carreau solutions, for both steady
and unsteady regimes, are depicted in Fig.
7
(velocity) and Fig.
8
(WSS). The
geometry considered for these results is the idealized with hole (clipped side-
branch), and the traction-free condition at this outflow boundary. The maximum
Fig. 7
Velocity magnitude (cm/s) for the clipped geometry with traction-free conditions at
the side-branch outflow, using the Newtonian (
top
) and the Carreau (
middle
) models, and its
differences (
bottom
), for the unsteady and steady solutions. The maximum difference is calculated
for the cross-section, using the maximum value for the percentage
Search WWH ::

Custom Search