Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
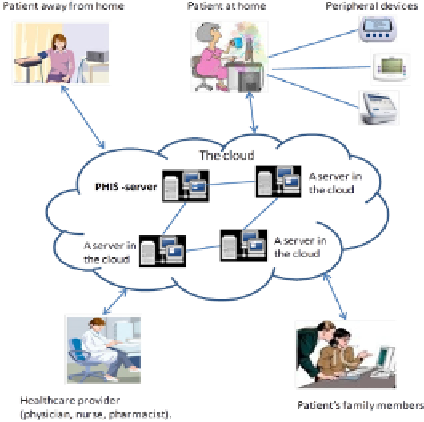
Fig
g. 2.
The users of the cloud-based PHIS
We next itemize some cl
larifying aspects of the figure:
vantages of SOA (Service Oriented Architecture) in
es, e.g., in importing patient's health data the PHIS-ser
vers of other healthcare organizations including hospit
lth centers.
the peripheral devices that the patient has at home are c
d so the vital signs collected by the devices are transmit
, to the PHIS.
or her health data stored in PHIS through the browser.
but an internet access, the patient can easily connect to
eing away from home.
d patient's family members that are authorized by the
ealth data as well as communicate through their browser
nal structure of the PHIS-server.
•
The cloud takes the ad
interoperation of the servic
interoperates with the serv
physicians' offices and heal
•
the
rver
tals,
As the figure illustrates t
nected to patient's PC, and
via the PC to the cloud, i.e.,
•
con-
tted
The patient accesses his
the patient needs nothing b
PHIS at home, as well as be
•
As
the
Healthcare providers and
tient can access patient's he
Next, we consider the intern
pa-
rs.
5
PHIS-Ontology
The architecture of the PHI
3. As the figure illustrates
access the PHIS-server thro
that provides personalized c
In designing the PHIS w
tions [20], where the key id
(stored in a knowledge bas
grating the ontologies of th
IS and its connections in the cloud are presented in Fig
s patient and the members of his or her healthcare te
ough the personalized health portal. It is a site on WW
capabilities for its users and links to other relevant serve
we have followed the idea of knowledge oriented organi
dea is to revolve all applications around a shared ontolo
se), which we call
PHIS-ontology
. It is developed by in
he e-health tools supported by the PHIS. For now we h
gure
eam
WW
ers.
iza-
ogy
nte-
have
Search WWH ::

Custom Search