Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The first aim of our research, which is presented in this paper, is to introduce a model
which predicts the patients HR on basis of information about the patient and the envi-
ronment. Secondly, we present a PHR system that uses a standardized data exchange
to parameterize the HR model by combining professional and user generated informa-
tion. The system also has the potential to overcome the acceptance problems of exist-
ing PHRs, by giving users the physical control about their health data.
2
Methods
2.1
Characteristics and Preparation of the Model Data
The data for the heart rate prediction model was obtained during outpatient rehabilita-
tion from cardiopulmonary patients with NYHA 1-2 and COPD level 2-3. The only
exclusion criterion was the inability to perform training.
We started with an original dataset of 164 patients (82 W, 82 M) and 1201 training
sessions, which were collected between July and September 2009 in the exercise
training center of the Medical School Hannover in addition to regular ambulatory
training sessions. Patients performed their sessions twice a week, whereas in mean
each patient performed ~8 training sessions (± 7.7). HR was obtained on basis of elec-
trocardiogram (ECG) data. The following additional data was available:
•
Patient demographics: age, sex
•
Training data: date and time, duration, load
•
Vital signs data: resting HR before training, recovery HR after training, blood
pressure (BP) (rest, load, recovery - systolic and diastolic), Borg value [16] (used
scale 6-20), HR during the whole training (sample rate ≈ 1 Hz.).
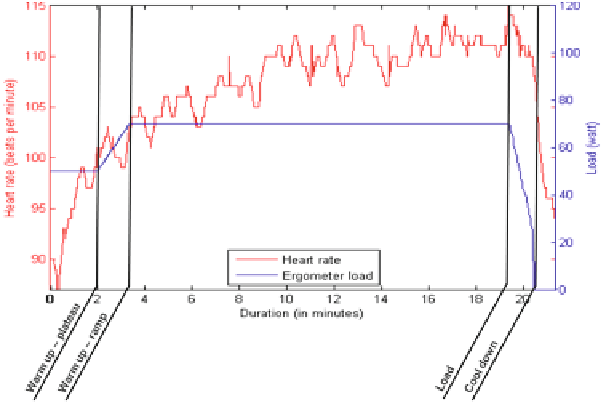
Fig. 1.
Sample training session with heart rate, training load and distinction into the four train-
ing phases
Search WWH ::

Custom Search