Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
magnitude of 0.5mm, or even lower [26] while data acquisition follows DICOM (Dig-
ital Imaging and Communications in Medicine). DICOM is the standard communica-
tion protocol for structuring and encoding medical reports [27] used by commercial
image manipulation software, required for converting multiple 2D images into a 3D
one.
After the representation of the model's outer surfaces, cortical and cancellous bone
properties have to be assigned. This can be directly achieved within the segmentation
software through accurate distinction of the two types based on their CT spectrum or
by considering both, the inner and outer cortex of the cortical bone.
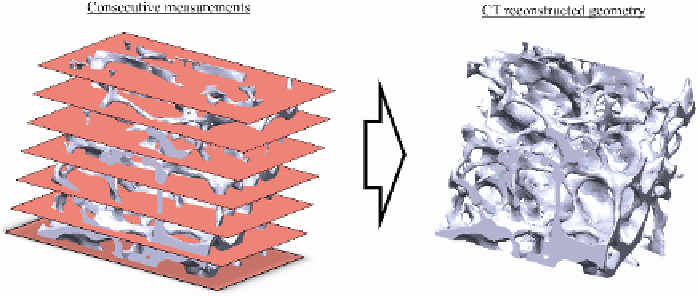
A reverse engineered cancellous bone model is illustrated in figure 1.
Fig. 1.
micro-CT based reconstruction of a cancellous bone model
2.2
MRI Based Reconstruction
MRI scanning is based on atoms magnetization rather than ionizing radiation used by
CT. This is particularly useful when trying to encapture tissue with many hydrogen
nuclei and little density contrast thus providing high accuracy even for soft tissue
images [28]. It is however a disadvantage, when attempting to reconstruct skeletal
models, as bone cannot generate a magnetic resonance signal, due to its severely short
1
H transverse relaxation times. Therefore the cortical bone is indirectly approximated
through the signal generated from the surrounding soft tissue which in most cases
leads to accurate results. This is even more complex, when attempting to reconstruct
cancellous bone, which must be considered through the reconstruction of the medullar
canal, which reproduces a notable contrast within the image [29]. This however, re-
quires extreme caution and experience in cases where interposing soft tissue is
present.
Alike to CT, data encoding in MRI, follows DICOM and the basic concept of re-
constructing 3D geometries remains similar [30] following two distinctive steps,
thresh-holding of the desired spectrums, to determine the bone contour within every
scan and overlaying of those to constitute the 3D geometry. The slice spacing howev-
er is slightly distanced when compared to CT imaging techniques [31]. This imposes
a further restriction as high accuracy models, like the one presented in figure 1, as
MRI models facilitate precise representation of cortical bone, whereas cancellous
bone must be considered as a homogene material with anisotropic behavior.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search