Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
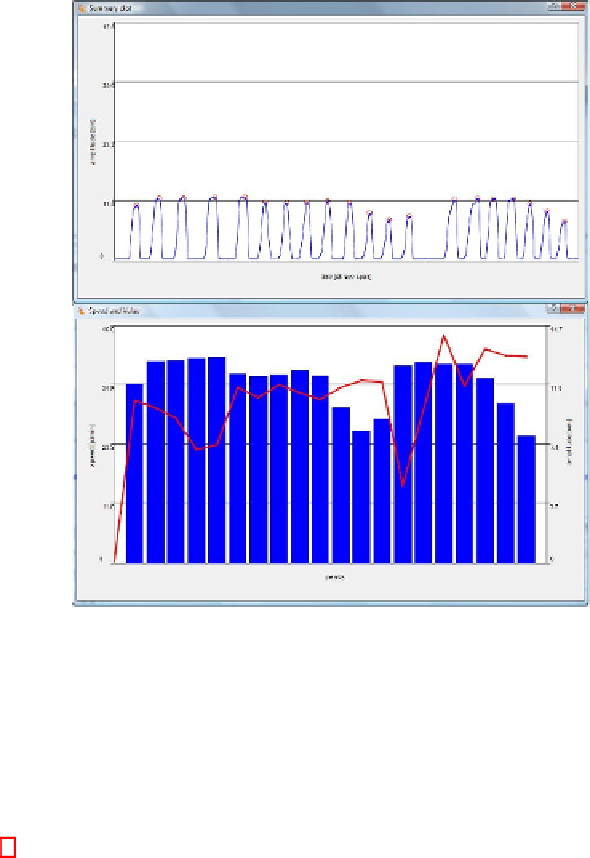
Fig. 7.
Marked whole signal plot (top) and “speed and value” plot (bottom) for the extension test
Three of them are affected by RA and suffered from muscular hypotrophy, capsular
and tendon sheats fibrosis of the hands and wrists without deformities. Before starting
the rehabilitation phase, they underwent a functional assessment through the traditional
tools and the portable prototypical device to test its ergonomics and functionality.
Traditional assessments of hand function were performed using the Dreiser test, the
HAQ, the ROM. For the latter, the movements leading to the hand positions presented in
Fig. 8 have been considered, namely wrist flex-extension, wrist lateral-lateral and finger
lateral-lateral. Hand extension ability was evaluated through the experimental device
and by traditional tools. The patient dexterity (exercise of dynamic rotation and finger
tapping exercise) and the rotation torque (isometric rotation exercise) were assessed
only by the experimental device since no instruments are currently available for such
evaluations. Demographic characteristics and results are shown in Tab. 1 and Tab. 2.
Although it is not possible to compare the results obtained with the traditional tools
against those recorded using the experimental device, because of the low number of
subjects, it is worth mentioning that the latter seems to fit with the former. As an ex-
ample, the SSc2 patient, who showed the highest Dreiser's and HAQ scores and the
poorest ROM and traditionally evaluated extension performances, due to high disabil-
ity levels, had the poorest performances at the finger tapping, dynamic rotation and
extension exercises evaluated through the experimental device. Since previous studies

Search WWH ::

Custom Search