Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
a
5.0e7
2.0e7
d
5.0e7
0.0
2.0
4.0
6.0
8.0
b
2.0e7
5.0e7
0.0
2.0
4.0
6.0
8.0
2.0e7
e
0.0
2.0
4.0
6.0
8.0
3.0e7
c
5.0e7
1.0e7
2.0e7
0.0
2.0
4.0
6.0
8.0
Time, min
0.0
2.0
4.0
Time, min
6.0
8.0
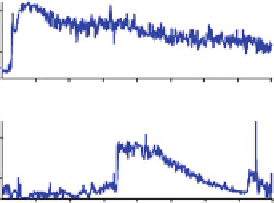
Fig. 2
(
a
) XIC of +Q1: 292.8-293.3 Da as EDTA from Indicating FTA Paper; (
b
) XIC of +Q1:
121.5-122.0 Da as Tris from Indicating FTA Paper; (
c
) XIC of +Q1: 59.8-60.3 Da as guanidine
thiocyanate from FTA Elute Paper; (
d
) XIC of −Q1: 57.75-58.25 Da as guanidine thiocyanate on
FTA Elute; (
e
) XIC of −Q1: 264.431-264.931 Da as SDS on Indicating FTA
spectrometry Q1 scanning in both positive and negative ionization modes. Two
disks (6 mm i.d. each) free from biological matrix for FTA Elute, Indicating FTA
and VWR 237 paper/cards were extracted. Two microliters of the reconstituted
solution was injected into the liquid chromatograph system. More than ten chemi-
cals were found to be present among pretreated paper/cards, but only a few typical
chemicals such as
tris
-hydroxymethyl aminomethane and sodium dodecyl sulfate
from Indicating FTA (DMPK-A), guanidine thiocyanate from FTA DMPK-B could
be clearly identified by matching the
m/z
of their molecular ions. Figure
2a-e
show
the extracted ion chromatograms for the representative
m/z
of the various chemical
components observed in the noted paper/cards. Figure
2a-c
were from positive ion-
ization scanning and Fig.
2d-e
were from negative ionization scanning. VWR 237
paper appears to be significantly cleaner than FTA Elute and Indicating FTA paper/
cards. According to the patent [
38
] covering the sampling cards, the coating materi-
als on sampling cards may include impregnating agents such as polystyrene, a weak
base, a chelating agent, an anionic detergent and optional uric acid/urate salt, pro-
tein denaturing agent, and a free radical trap, etc.
Most of the chemicals found on the FTA Elute and Indicating FTA paper/cards
are believed not to be friendly with LC-MS because these chemicals affect the accu-
rate quantitation of target analyte in the manners of ionization suppression, enhance-
ment or matrix effect when they are co-eluted with the target analytes or even
distortion of the chromatography by prolonged retention or accumulation. Therefore,
the impacts of these water-soluble chemicals on the quantitation of the target ana-
lyte must be carefully evaluated in the development of any DBS-LC-MS method, a
general approach is to minimize or eliminate the co-elution of these compounds by
separating these chemicals from the target analyte using liquid chromatography.
Depending on the compounds used to impregnate the cards that may be easily