Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CH
3
H
2
N
O
N
CH
3
CH
3
HN
O
O
O
CH
3
Phencyclidine
Ketamine
Mescaline
CH
3
CH
3
N
R
CH
3
OH
H
O
H
H
3
C
H
3
C
CH
3
O
N
H
R
-H
D
9
-tetrahydrocannabinol(THC)
Psylocine
-OPO
3
H
2
Psylocibine
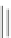
Fig. 5
Structures of the main hallucinogens
5.1.1
Pharmacodynamics
Mescaline acts similarly to other psychedelic agents. It activates the serotonin
5-HT2A receptor with a high affinity as a partial agonist. This receptor activation
causes the release of glutamate in the prefrontal cortex and optic nerve correlated
with cognitive and perceptual distortions.
5.1.2
Effects
The effects of the mescaline are strongly dose-dependent and occur 2 or 3 h after
intake and last up to 12 h. Hallucinogenic effects are accompanied by states of
excitement, insomnia, feelings of omnipotence, and logorrhea [
20
] .
5.1.3
Pharmacokinetics
Mescaline is rapidly absorbed by the human organism, especially after oral intake.
About 90 % of the dose is excreted in the urine within 24 h after intake. 39 % is found
as an acid 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylacetic, inactive, and the remaining percentage