Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
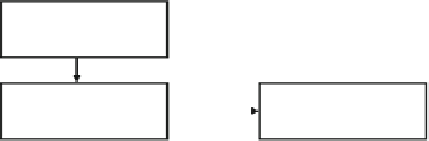
PCI w/stent
sensitive
wildtype
clopidogrel
aggregometry
standard dose
resistant
wildtype
resistant
carrier
Alternate anti-platelet
medication
Increase dose
Fig. 4
Proposed testing algorithm for clopidogrel therapy for acute coronary syndromes
of the parent drug. However, IMs and PMs may experience a lack of efficacy from
some opioids (i.e., codeine) because of their inability to form the active metabolite
(i.e., morphine). The majority of individuals are
CYP2D6
EMs; however, 7-10 % of
the Caucasian population and 1-4 % of other ethnic populations have nonfunctional
alleles [
29,
30
] .
CYP2D6 is the most well studied gene with respect to the pharmacogenetics of
codeine metabolism. Approximately 50-70 % of codeine is glucuronidated to
codeine-6-glucuronide by UGT2B7 and 10-15 % is
N
-demethylated to norcodeine
by CYP3A4 [
31
]. Compared to codeine both metabolites have a similar affinity for
the m-opioid receptor. A smaller percentage of codeine (0-15 %) is
O
-demethylated
to morphine which has a 200-fold increased affinity for the m-opioid receptor com-
pared to codeine. PMs may not experience adequate pain relief since they are unable
to convert codeine to morphine, while UMs may experience morphine intoxication
as a result of rapid conversion of codeine to morphine.
Multiple pharmacogenetic studies have shown that there is significant variability
in both the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of codeine and that its analge-
sic effects are mostly dependent on metabolism to morphine [
32-
35
] . However,
many of these studies were small and had a limited sample-size. Large-scale studies
are still needed to demonstrate impaired analgesic outcome in
CYP2D6
PMs. In
2002, Williams and colleagues investigated the postoperative analgesic efficacy in a
pediatric population (
n
= 46) by determining genotype, phenotype and morphine
production from codeine [
32
]. They found that there was a significant relationship
between phenotype and plasma morphine concentration after administration of
codeine, however, no relationship was found between phenotype and analgesia.
This could be a result of experimental cofounders such as coadministration with
diclofenac. Another study found that
CYP2D6
UMs (
n
= 12) had approximately
50 % higher plasma concentrations of morphine and its glucuronides compared
with EMs (
n
= 11) after administration of a single dose of 30 mg codeine [
33
] . Only
half of the
CYP2D6
EMs felt sedation from the codeine compared to 91 % of the