Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
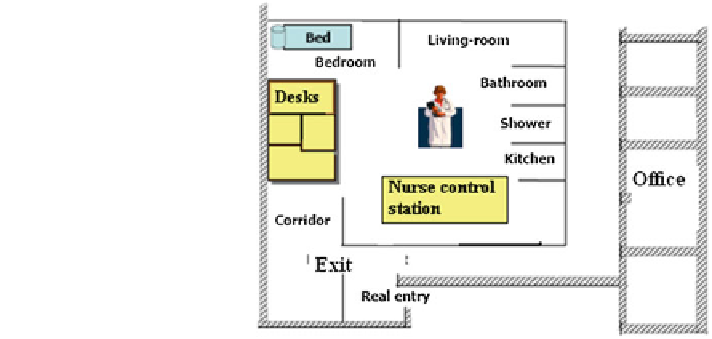
Fig. 2 Layout of the
experimental smart health
home at UVA
continuous medical history. Unobtrusive area and environmental sensors combine
with wearable interactive devices to evaluate the health of spaces and the people
who inhabit them. Authorized care providers may monitor resident's health and
life habits and watch for chronic pathologies. Multiple patients and their resident
family members as well as visitors are differentiated for sensing tasks and access
privileges.
High costs of installation and retrofit are avoided by using ad hoc, self-
managing networks [
2
,
3
]. Based on the fundamental elements of future medical
applications (integration with existing medical practice and technology, real-time
and long-term monitoring, wearable sensors and assistance to chronic patients,
elders or handicapped people), our wireless system will extend health care from
the traditional clinical hospital setting to nursing and retirement homes, enabling
telecare without the prohibitive costs of retrofitting existing structures. Figure
2
shows the layout of the experimental laboratory. The architecture is multitiered,
with
heterogeneous
devices
ranging
from
lightweight
sensors,
to
mobile
components, and more powerful stationary devices.
The advantages of a WSN are numerous for smart health care, as it
provides the following important properties:
1. Portability and unobtrusiveness: Small devices collect data and communicate
wirelessly, operating with minimal patient input. They may be carried on the
body or deeply embedded in the environment. Unobtrusiveness helps with
patient acceptance and minimizes confounding measurement effects. Since
monitoring is done in the living space, the patient travels less often; this is safer
and more convenient.
2. Ease of deployment and scalability: Devices can be deployed in potentially
large quantities with dramatically less complexity and cost compared to wired
networks. Existing structures, particularly dilapidated ones, can be easily
augmented with a WSN network, whereas wired installations would be
expensive and impractical. Devices are placed in the living space and turned on,
self-organizing and calibrating automatically.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search