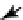Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Other
gradient(s)?
Wnts?
Global module
Ds
Fj
Ft
Flamingo
Core
module
Frizzled
Van Gogh
Dishevelled
Diego
Prickle
Prehair
Effectors
Proximal
Distal
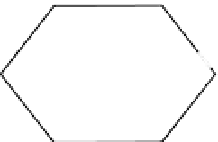
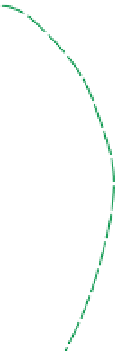
Figure 2.1 Hierarchical model of the PCP signaling pathway. The pathway consists of
three modules, the global-, core-, and tissue-specific effector modules. According to the
series model, the global module provides directional input to the core module (blue
arrow) that establishes and amplifies subcellular asymmetry. This subcellular asymmetry
is used to direct tissue-specific effector module function within the cell. According to the
parallel model, the global module communicates directly with the tissue-specific effec-
tor module (green dashed arrow), without signaling to the core module. Directional
information for the global module comes from tissue-level expression gradients of
Ds and Fj, but it is likely that other gradients are also important, at least in the wing
(black dashed arrow). While Wnt proteins seem not to play a direct role in PCP signaling
in Drosophila, they appear to do so in vertebrates (gray dashed arrows). Precisely, how
Wnts affect vertebrate PCP is unclear. Asymmetrically segregated core PCP proteins are
shown. Various effector modules produce different tissue-specific responses. Here, ef-
fectors establish the distal
location for growth of a prehair, as on the wing and
abdomen.
is enriched on the anterior cortex, while Fz is predominantly localized on the
posterior side of the SOP cell. Their asymmetric localization predefines
the anterior/posterior membrane domains, which subsequently determine
the axis of SOP division and the asymmetric distribution of determinants
of the daughter cell fates (
Bellaiche et al., 2004, 2001
).
The generality of such polarized protein localization was supported by
recent investigations on various vertebrate epithelia. In the ventral node
of early mouse embryos, restricted localization of Vangl1, Vangl2, Pk2,