Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
A
B
Facial primordia
Wnt5a
Tail bud
Tongue
P
Vangl2
Wnt5a gradient
C
Neural tube
Neural tube
Neural tube
Wnt11
Wnt11
Wnt11
Wnt11
Wnt11
Wnt11
Wnt11
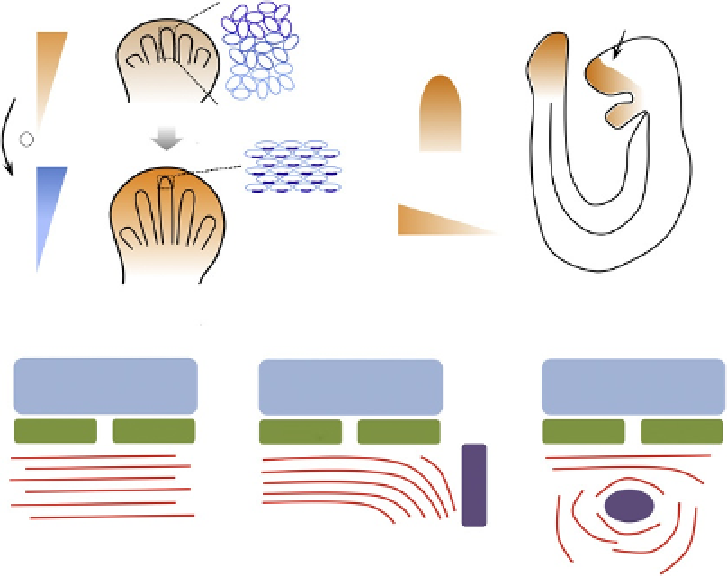
Figure 11.1 Instructive role of Wnt morphogen gradient in establishing tissue polarity.
(A) In the developing limb bud, by inducing different levels of Vangl2 phosphorylation
(blue), Wnt5a gradient (orange) is translated into an activity gradient of Vangl2. Such
activity gradient then induces its protein asymmetrical localization (blue) leading to
the downstream polarized cell behaviors. (B) Wnt5a is expressed in a gradient in the
branchial arches, tail bud and tongue tip. Wnt5a may play similar roles in elongation
of these tissues as Wnt5a
/
embryos exhibited PCP defects in these places. (C) Muscle
fibers parallel and align with neural tube and the Wnt11 expression area. If Wnt11-
expressing cells were placed between two somites or within the myotome (purple),
muscle fibers will be reoriented to the ectopic Wnt11.
parallel to the neural tube. It is shown that Wnt11 expressed in the chick
neural tube is necessary and sufficient to orient muscle fibers through core
PCP proteins (
Fig. 11.1C
)(
Gros, Serralbo, & Marcelle, 2009
). It has been
demonstrated that PCP controls oriented cell division in tissue elongation
(
Gong, Mo, & Fraser, 2004
). In mouse kidney morphogenesis, Wnt9b is
found to be necessary for CE processes and polarized divisions of kidney
epithelial cells that determine the tubule diameter. Attenuation of Wnt9b
signaling affects the PCP leading to significantly increased diameter of
kidney tubules (
Karner et al., 2009
). In the collecting duct epithelium of