Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Cell A
Cell B
PDZ
Dvl
Vangl
Fz
PDZ
Pk
PDZ
PDZ
Celsr1
Celsr1
Scribble
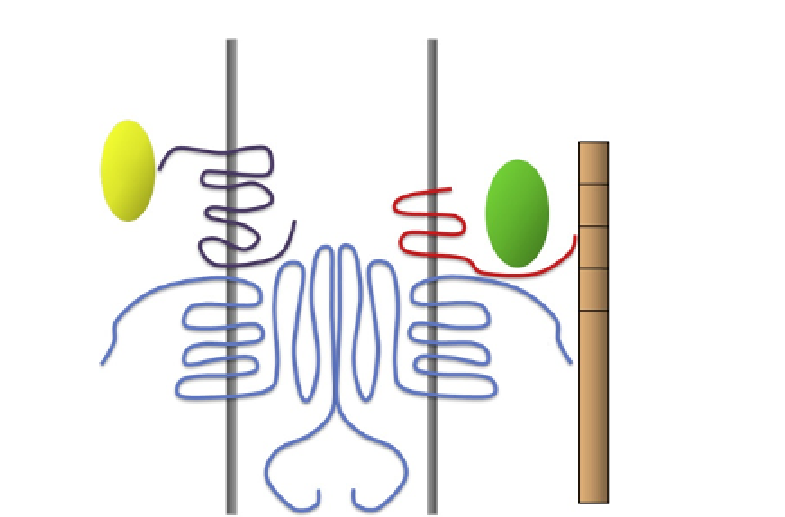
Figure 10.4 Schematic representation of proposed Vangl2-dependent PCP complexes
in mammalian cells. The intracellular carboxyl terminal domain of Vangl2 has been
shown to interact with the cytoplasmic protein Pk and a cytoplasmic segment of
membrane-bound Celsr1. The intracellular carboxyl terminal domain of Vangl2 also
interacts with the PDZ domains of the cytoplasmic protein Scribble. Cytoplasmic
domains of Celsr1 protein molecules from adjacent neighboring cells form homotypic
extracellular complexes.
neighboring cells (different variations of this model may be active in different
cell types) (
Fig. 10.4
). PCP signaling further requires an interactionbetween the
PDZ-binding domain of Vangl2 and the PDZ-domain of Scribble
(
Montcouquiol et al., 2006
).
A recently discovered Sec24b protein is needed for maturation of Vangl2
positive COPII vesicles and controls membrane targeting of Vangl2 to
membrane PCP complexes (
Merte et al., 2010; Wansleeben et al., 2010
).
Sec24b
mouse mutants display craniorachischisis and inner ear defects, and
Lp-
associated Vangl2 mutant proteins cannot enter COPII vesicles for
Sec24b-dependent maturation. In addition, there is an aberrant
localization of Vangl2 in Sec24b mutant embryos
in vivo
(
Merte et al.,
2010; Wansleeben et al., 2010
).
Importantly, a unique and critical feature of Vangl2 is that its function
represents a key rate-limiting and dosage-sensitive step in the PCP signaling.
Heterozygosity for
Vangl2
mutation (
Lp/
þ
) sensitizes the PCP pathway and