Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
A
B
nV
VII
nVI
nVII
Celsr1
ko/ko
WT
C
D
Celsr2
Dgen/Dgen
& Celsr2
Dgen/Dgen
; Celsr1
ko/ko
Celsr2
Dgen/Dgen
; Celsr3
ko/ko
& Fzd3
ko/ko
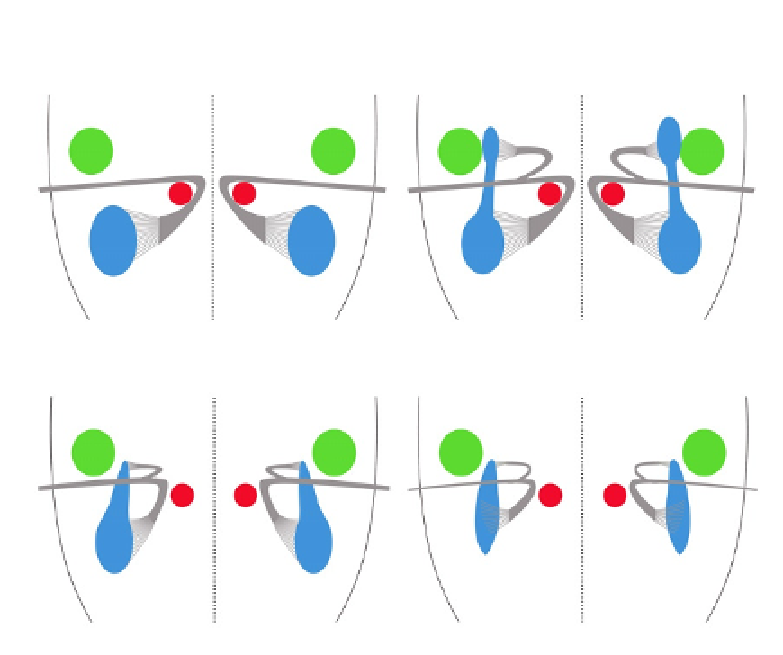
Figure 7.4 Migration of facial branchiomotor (FBM) neurons in normal and Celsr1
-
3
knockout mice. Drawings summarize the phenotype at P0. In wild-type animals (A),
FBM neurons form a single nucleus (nVII) in a region that derives from r6. Their axons
loop around the abducens nucleus (nVI) before exiting the rhombencephalon dorsally,
caudal to the trigeminal nucleus (nV). In Celsr1
ko/ko
mutants (B), in addition to the normal
nVII, FBM neurons form another ectopic nucleus at the level of nV, but their axons leave
the rhombencephalon at the right position. This is due to aberrant migration of FBM
neurons in lateral r2 during embryogenesis. In Celsr2
Dgen/Dgen
and Celsr2
Dgen/Dgen
;
Celsr1
ko/ko
(C), the facial nerve genu is completely abnormal and axons do not loop
around nVI because FBM neurons migrate prematurely in lateral r4-r5, forming lateral
heterotopias. In Celsr2
Dgen/Dgen
; Celsr3
ko/ko
and in Fzd3
ko/ko
, in addition to the absence of
the genu of the facial nerve, the size of nVII is reduced because of embryonic cell death
(D). “r,” rhombomere; nV, motor trigeminal nucleus; nVI, abducens nucleus; nVII, facial
nerve nucleus.
even rostral to the trigeminal (nV) nucleus but send their axons normally in
the facial nerve (
Fig. 7.4B
). In the hindbrain,
Celsr1
is expressed in
progenitors and in the floor plate, but not in postmitotic FBM neurons.
Consistent with this, conditional inactivation of
Celsr1
in progenitors
under
Nk6.2-Cre
recombination induces abnormal rostral migration,
whereas its deletion in FBM neurons using
Isl1-Cre
does not.