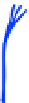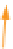Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(
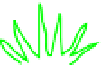
Fig. 6.5A and B
). Looking into the molecular and cellular anatomy of the
growth cone, the growth cone, particularly the filopodia, has similar com-
positions as adherens junction. Growth cones have both aPKC and
N-cadherin in the filopodia. N-Cadherin is found in adherens junctions
in chick cardiac muscle cells and lens epithelium (
Volk & Geiger, 1984,
1986
). Cadherins also interact with aPKC and regulate its activity and
A
Planar polarity
E-cad
Apical
aPKC
Basal
Planar polarity
B
Vangl2
N-cad
Apical
+
+
+
+
+
+
aPKC
+
Basal
C
Netrin-1
Semaphorin
Slit
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
PlexinA-1/
PTK7/
PCP
aPKC/
Par3/Par6
(apical-
basal)
Robo/
N-cad
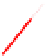
Figure 6.5 A cell polarity-signaling-based machinery for growth cone turning. (A) In ep-
ithelia, E-cadherin and aPKC defines the apical basal polarity and planar polarity is per-
pendicular to apical
-
basal axis. (B) In neuronal growth cones, N-cadherin and aPKC may
define the distal
-
proximal (apical
-
basal) axis and PCP signaling may be asymmetrically
activated in a subset of filopodia and steer turning in axis perpendicular to the distal
-
proximal
(apical
-
basal) axis.
(C) Other axon guidance signaling may access this