Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
one of the few mammalian tissues in which asymmetric localization of PCP
proteins can be observed. Finally, because less profound deviations in bundle
orientation can be quantified fairly easily, analysis of PCP defects in inner ear
can be used to assess the strength of different PCP mutants and to determine
potential additive effects of genetic interactions.
3. MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF PLANAR CELL
POLARITY
Genetic studies in
Drosophila
initially identified a core set of proteins
required for regulation of PCP (
Fig. 5.3
). These regulatory proteins signal
sequentially to integrate directional cues with cellular factors to direct
W
nt
Wnt
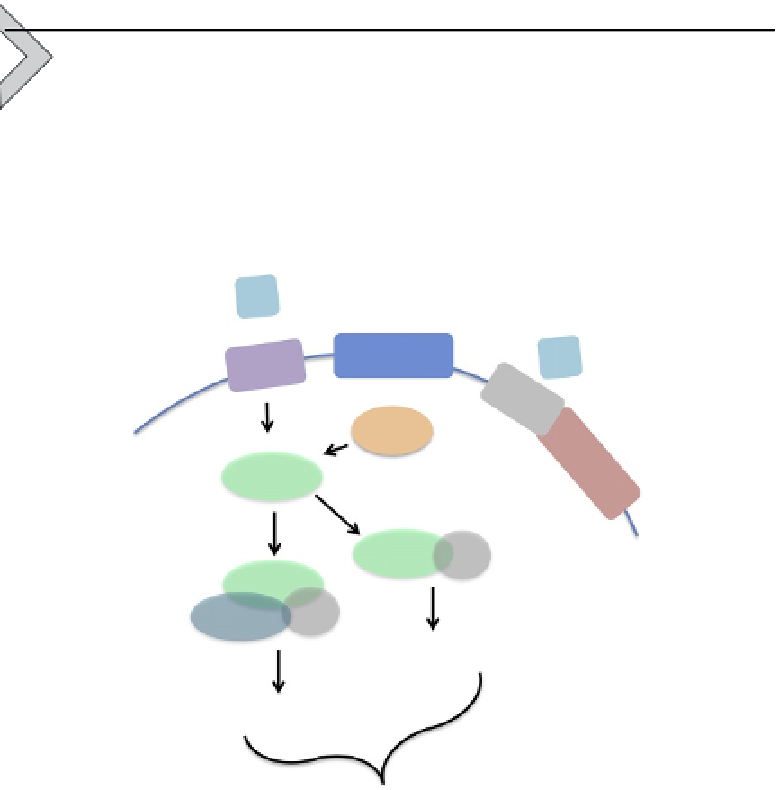
Figure 5.3 Molecular basis of PCP (noncanonical Wnt) signaling. Core components of
the planar cell polarity (noncanonical Wnt) signaling pathway. In vertebrates, PCP sig-
naling is initiated by the binding of Wnt ligands to membrane bound receptors (Fz) or
through complexes with coreceptors (Vangl1/2, Ror2, and Ptk7). The signal is trans-
duced via the assembly of various Dvl/effector complexes (Dvl1/2/3; Pk1/2/3), which
ultimately lead to the activation of various pathways regulating the actin cytoskeleton
and cell adhesion. Association of Dvl with Rho and Rac activates Rho Kinase (Rock) and
c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Activation of PLC, PKC, and Cdc42 is mediated via asso-
ciation with intracellular Ca
2þ
.