Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
in order to set it to the minimum in all cases and avoid erratic
behavior of LSM. Detection range is given by the arterial model
cross section diameter, because if this limit is not respected there is
a chance of missing a reference point during the catheter insertion.
Setting the detection range to the minimum for all the reference
points, warrantees that reference points placed in different vascular
branches will not produce erratic robot behavior.
P'
4
Reference Poin
ts
Catheter Motion
System Reaction
Point Detected
25
Insertion
Extraction
Bifurcation on path
Branch not leading to target
Target
Detection
range 6mm
20
P'
3
15
P'
1
P'
0
P'
2
10
5
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
Coronal Axis (mm)
Figure 7.20
Magnetic motion capture sensor trajectory graph for the
trajectory reconstruction with ACIS [16].
The detection range
d
n
is decided when building the sparse LUT,
for a probability of 1 to detect a reference point inside a model of
cross section diameter
d
,
d
n
should calculated from Eq. 7.8:
(7.8)
where
a
c
is the catheter cross section radius. As its seen
d
n
tends to
a
c
as the cross section diameter of the model is reduced, but this error
is the most important one for aorta's model experiment.
LSM's motion of insertion or extraction is not continuous in
time. At the one-dimensional path reconstruction experiment, every
insertion and extraction cycle is represented on the plot by a step of
6 mm length for all the segments of the path (Fig. 7.18). The length of
this step,
C
0
n
parameter, affects the accuracy of the system to change
the motion when a reference point is detected. Reducing
C
0
n
implies
a larger time of insertion because less catheter will be inserted
per LSM cycle as seen in Fig. 7.18.
C
0(
n-
1)
is the step length of LSM
conigured at the point
P
(
n-
1)
. The error introduced by
C
0(
n-
1)
in
P
n
is not reduced increasing the sampling frequency of the magnetic
tracker because the LSM only allows changing the direction of
insertion or twisting the catheter in some speciic points of the linear
motion cycle without losing synchrony or losing the torsion applied
to the catheter, respectively. Therefore, even if several samples are
dda
n
c

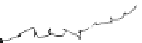


























































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search