Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
V1
5V
V2
+12V
V3
-12V
+V
1000uF
1000uF
1000uF
C9
C8
C7
R20
10k
A
na
l
og
D
CV
S1
R21
1k
10k
10k
10k
10k
C5
1uF
U1
But
t
on
s
16F877A
Vpp
A0
A
A2
A
A4
A5
E
E1
E2
Vdd
Vss
OSC0
OSC1
C0
C1
C
C3
D0
D1
B6
B7
B
B5
10k
B
B3
B1
1
u
F
Vd
B0
1uF
Vss
PC Interface
D
D7
D5
C
D4
+
-
+
-
C6
C
C5
V4
D2
D3
PW
M1
PWM
2
DC5
V
D
C5
V2
D
C5
V4
D
C5
V3
I
2
C
D
C
5
V
5
DC5V1
C4
1uF
U3
MAX232
C1+
VS+
C1-
C2+
C
2-
VS-
T2O
R2I
R2O
T2I
T1I
R1O
R1I
T1O
GND
Vcc
M
2
CCW
M
1
CW
C1
1uF
M
3
CCW
M
3
CW
M2
CW
M
1
CCW
C2
1uF
C3
1uF
Q12
NPN
Q11
NPN
Q10
NPN
Q9
NPN
Q6
NPN
Q8
N
PN
R8
1k
R7
1k
R12
1k
R11
1k
R10
1k
R9
1k
M
5
C
C
W
M
4C
W
M
6
C
C
W
M
6C
W
M
5C
W
M
4
CCW
Q7
NPN
Q5
NPN
Q1
NPN
Q2
NPN
Q3
NPN
Q4
NPN
R5
1k
R6
1k
R1
1k
R2
1k
R3
1k
R4
1k
Figure 7.4
Circuit design for robotic camera control.
The three degrees of freedom are initialized using optical limit
switches and then controlled using step count. The designed circuit
offers an interface with a joystick and a serial port. The joystick
allows a simple human interface to manipulate the three DOFs
without the need of a computer. The serial port offers an option for
controlling the Robotic Camera from the PC or by other electronic
circuits. All those systems were integrated in printed circuit board.
Additionally, an interface using foot pedals was built for controlling
the image processing for the IVR environment simulation (Fig. 7.4,
Table 7.2).
7.3 Robot Manipulation
7.3.1
Silicone Models of Vasculature
As the target of the robotic camera is to simulate endovascular
surgery and catheter shaped coils are used, a silicone model of major


























































































































































































































































































































































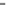
































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search