Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
At irst, mass
M
of this minute luid body is
M
=
ρδxδyδz
(5.10)
and acceleration is obtained from substantial derivative of velocity.
That is
u
u
u
u
t
u
u
u
x
u
u
u
y
u
z
Du
Dt
B
x
u
u
v
w
(5.11)
u
u
u
v
t
u
u
v
x
u
u
v
y
v
z
Dv
Dt
B
y
u
u
v
w
(5.12)
u
u
u
w
t
u
u
w
x
u
u
w
y
w
z
Dw
Dt
B
z
u
u
v
w
(5.13)
Force acting on luid without viscosity (ideal luid) is just only
mass force and pressure. Pressure
p
works in the direction of
internally normal stress toward a plane. As a difference of pressure
acting on two faces with a distance
δx
perpendicular to
x
axis, the
external force in the
x
axis is
E
x
E
x
EE
{( -
px
, , ,)- {(
y zt
ppx
, , ,)}
y zt
y z
(5.14)
2
2
u
p
2
EEE E EE
-
xyz O
((
x
) )
yz
u
x
z
px
x
2
,
y
,
z
z
x
y
x
2
,
y
,
z
px
+
y
x
Figure 5.3
Pressure acting on a surface of luid body.




















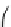









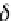
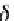





























































Search WWH ::

Custom Search