Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
2.2 Pathophysiological Relevance of Meprins
Both meprins are able to process compounds of the extracellular matrix such as
laminin-V, collagen IV, fibronectin, or nidogen 1, but also growth factors,
cytokines, and peptide hormones, including bradykinin, angiotensins, and
gastrin.
51-54
Furthermore, the ability of meprin b to activate IL-1b and IL-18
reveals the protease to be pro-inflammatory.
40,49,50,55
Taken together, these
findings suggest a contribution of meprins to epithelial differentiation, matrix
remodeling, and cell migration.
However, there are still many open questions concerning the pathophysio-
logical relevance of meprin a and b. Recent studies provide strong evidence for
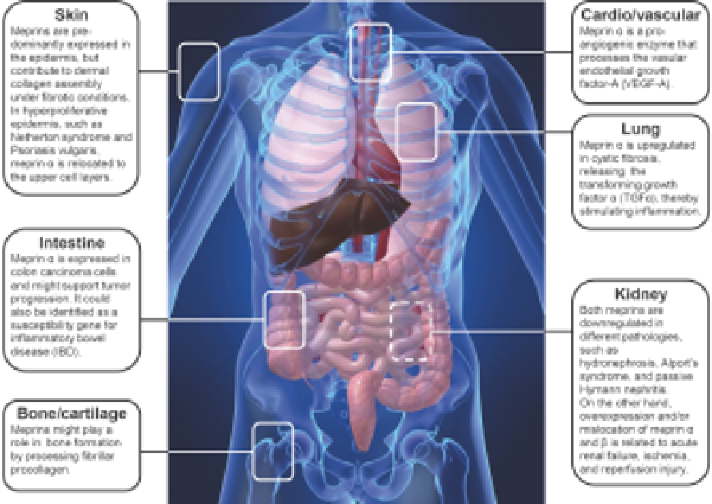
functions in inflammation, angiogenesis, cancer, and fibrosis (Figure 2.4), to be
described in detail below.
2.2.1
Inflammatory Disease
2.2.1.1 Nephritis
Over recent decades, meprins were thought to be expressed predominantly in
kidney and intestine, owing to the high amounts of these enzymes detected in
these tissues in mice.
56
Although the expression profiles differ between rodents
and humans, the focus of meprin research has emphasized pathophysiological
conditions in these organs. Hence, many studies deal with different forms of
Figure 2.4
Distribution of meprin a and b under pathophysiological conditions.