Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
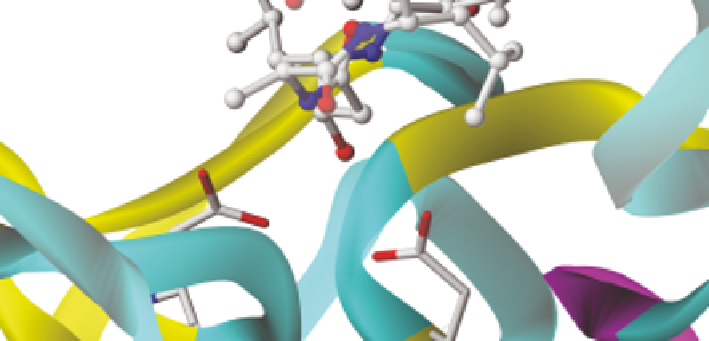
Figure 11.6
Close-up of the active site binding of pepstatin to Plasmodium falciparum
plasmepsin II (PDB: 1SME, Baldwin et al.
118
). The oxygen atom from
the amino acid statine fits into the space between the two catalytic
aspartic acids and forms hydrogen bonds to both, 2.83 A
˚
in one case and
2.60 A
˚
in the other. This provides tight binding and accounts for the very
low K
i
value exhibited by pepstatin with aspartic proteinase in general.
developed a methodology to determine to a high degree of precision the ther-
modynamic parameters for inhibitor binding to plasmepsins as well as other
enzymes.
86
Professor Kiso's laboratory provided the synthetic expertise to prepare, lit-
erally, thousands of peptidomimetic compounds for testing against plasmepsins
and other proteolytic enzymes.
80,82,83,87
In addition to the long-term colla-
boration with the Freire group, compounds from the Kiso group have been
shared with other labs to permit crystallization with several plasmepsins.
26,46,88
The next group to highlight is from Uppsala, Sweden and is led by Anders
Hallberg, with colleagues Mats Lahred, Johan Aqvist, Martin Nervall, Hugo
Gutierrez-de-Teran, and Bertil Samuelsson.
89-101
The author of this chapter
was privileged to collaborate on several of these studies.
93-96,101
In addition to
synthesis of a variety of inhibitors with varying scaffolds to test theories of the
requirements for strong binding, the Uppsala group also conducted extensive
computational studies to rationalize the resulting inhibition data, leading to
new insights into active site binding. Many of the compounds synthesized
contained either the -CH
2
-CHOH- or the -CHOH-CHOH- isosteres, which
typically provides tight binding. Another group utilizing computational
methods to design inhibitors for plasmepsins is that of Gerhard Klebe in
Marburg, Germany.
102-106
In addition, computational screening in the
laboratory of Wibke Diederich107 led to the design of a 2,3,4,7-tetrahydro-1H-
azepine scaffold that resulted in several submicromolar inhibitors that were
selective for different aspartic proteinases.
107
Daniel Bur of Actelion Pharmaceuticals has pursued inhibitor design for
several enzymes in the aspartic peptidase class, including renin and the malaria