Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
O
H
H
N
H
H
N
H
2
N
NH
2
H
O
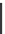
9.13
NH
N
N
Cl
O
HN
H
2
N
O
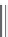
9.14
NH
N
NH
O
O
NH
2
NH
2
H
2
N
O
9.15
NH
Finally, derivatives of aminopyridine (General Structure 9.16, Figure 9.3),
such as the (R)-2-amino-3-methyl-pentanoic acid {(S)-1-1[(6-amino-pyridin-
3-ylmethyl)-carbamoyl]-2-naphthalene-1-yl-ethyl}-amide (compound 9.17) and
the (R)-3-methyl-2-methylamino-pentanoic acid [(S)-1-[(6-amino-pyridin-3-
ylmethyl)-carbamoyl]-2-(3,4-dichloro-phenyl)-ethyl]-amide (compound 9.18),
were developed recently as novel KLK1 inhibitors for the treatment of asthma,
inflammatory conditions, cancer, etc. These compounds showed highly potent
and selective activity against KLK1. Specifically, 9.17 and 9.18 have an IC
50
of
960 and 220 pM, respectively, while they are 410 000 times more selective when
compared to plasma kallikrein, thrombin, trypsin, and plasmin.
107
9.4.2 KLK3/PSA Inhibitors
KLK3/PSA has long been a target for inhibitor development, and several groups
have made various attempts to design novel inhibitors. An early approach aimed
to develop new inhibitors was based on 2-azetidinone analogs (General Formula
9.19) and led to the identification of 9.20 that exhibited a relatively high IC
50
of
8.98 mM.
108
Later studies used 9.20 as a lead compound and synthesized 9.21
with potent inhibitory activity against KLK3/PSA and an IC
50
of 226 nM [for
the (S, S) isomer].
109
9.21 in racemic mixture has a low IC
50
of 340 nM.
110
These