Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
12
10
Control ( )
CA074 ( )
CA074Me (
)
8
E64c (
)
6
4
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
Hour
(b)
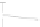
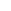
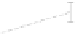
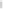
Figure 6.4
Inhibitors of cathepsin B reduce Ab production in the regulated secretory
pathway of neuronal-like chroman cells. (a) Inhibition of Ab production
in regulated secretory vesicles by cathepsin B inhibitors. The effects of
cathepsin B inhibitors, CA074 (10 mM,
E
) and CA074Me (10 mM,
&
), on
the production of Ab40 from endogenous APP in regulated secretory
vesicles isolated from chroman cells was evaluated in time-course studies.
Controls without inhibitors (
K
), or with the cysteine protease inhibitor
E64c (10 mM,
J
), were included. Each inhibitor was tested in triplicate;
values represent x
SEM. (b) Reduction in Ab production in the major
regulated secretory pathway by cathepsin B inhibitors. Neuronal-like
chroman cells (bovine) were treated with the inhibitor CA074Me (50 mM)
for 18 h. Regulated secretion (R) was induced by KCl (50 mM) for 15 min,
and Ab40 was measured in secretion media. Secretion by the regulated
secretory pathway (R) is represented by KCl-stimulated secretion. Basal
secretion (no KCl) represents secretion from the constitutive secretory
pathway (C). The results show a significant reduction by CA074Me of Ab
secreted from the regulated secretory pathway, with *p
o
0.05 (Student's
t-test).
41
in the London mutant APP mouse model of AD, which has an APP mutation
at the g-secretase site sequence (V717I) which was under the control of the thy1
promoter.
42
Administration of the CA074Me and E64d inhibitors both resulted
in substantial improvement in memory deficit in the London AD mouse model,
assessed by the Morris water maze memory test that measures latency time to