Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
blood count in the bloodstream. They have segmented nuclei and are “C” shaped. Neutro-
phils can be most commonly found near sites of infection or injury, where they will stick to
the walls of the blood vessels and engulf any foreign particles that try to enter the blood-
stream. They can also be found in the pus of wounds.
Eosinophils make up 2 to 5 percent of the total blood count and mainly attack parasites
and any antigen complexes. These cells are also responsible for allergic response within the
blood. Basophils make up less than 1 percent of the total white blood count. They secrete
anticoagulant and antibodies, which mediate hypersensitivity reactions within the blood.
They are known to have phagocytory features, although they are more often related to
immediate immune reaction against external germs and diseases. Monocytes, having only
5 to 8 percent of the total white blood count, are the largest of the five types of white blood
cells. They act as tissue macrophages and remove foreign particles and prevent the invasion
of germs that cannot be effectively dealt with by the neutrophils. They have been known to
have phagocytic functions.
Lymphocytes produce antibodies against toxins secreted by bacteria and infecting germs.
These antibodies will be excreted into the plasma to kill bacteria in the blood as well as act
as antitoxins. These antibodies will cause the foreign particles to cluster together, rendering
them easily engulfed by the phagocytes. However, the nature of lymphocytes is highly spe-
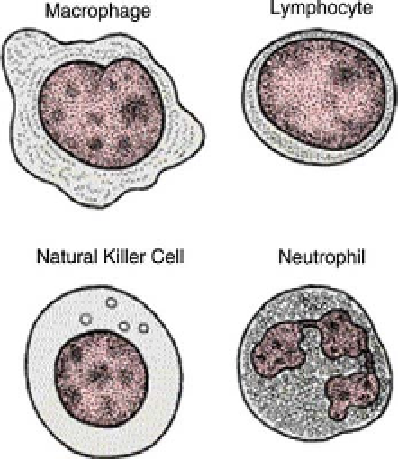
cific, and they can recognize only certain antigens. Figure 14.28 shows several white cell
subtypes.
Platelets are only about 20 percent of the diameter of red blood cells, the most numerous
cell of the blood. The normal platelet count is 150,000-350,000 per microliter of blood, but
since platelets are so small, they make up just a tiny fraction of the blood volume. The prin-
cipal function of platelets is to prevent bleeding. Platelets are produced in the bone marrow,
the same as the red cells and most of the white blood cells. Platelets are actually not true
cells but merely circulating fragments of cells. But even though platelets are merely cell
FIGURE 14.28
Sizes and shapes of various white cell types.