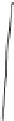Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CRANIAL DIRECTION
FRONTAL PLANE
SAGITTAL PLANE
MIDSAGITTAL PLANE
TRANSVERSE PLANE
CAUDAL DIRECTION
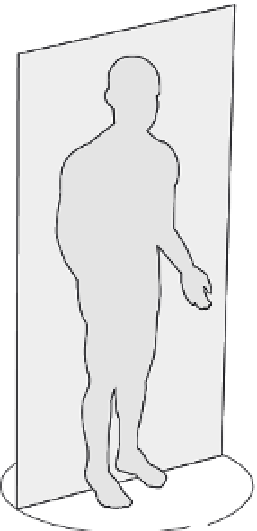
FIGURE 3.2
The body can be divided into sections by the frontal, sagittal, and transverse planes. The midsag-
ittal plane goes through the midline of the body.
whereas those parts that lie in the direction of the feet are said to be in the caudal direction
(Figure 3.2).
Anatomical locations can also be described in terms of planes. The plane that divides
the body into two symmetric halves along its midline is called the midsaggital plane
(Figure 3.2). Planes that are parallel to the midsaggital plane but do not divide the body into
symmetric halves are called sagittal planes. The frontal plane is perpendicular to the mid-
saggital plane and divides the body into asymmetric anterior and posterior portions. Planes
that cut across the body and are perpendicular to the midsaggital and frontal planes are
called transverse planes.
Human bodies are divided into two main regions: axial and appendicular. The axial part
consists of the head, neck, thorax (chest), abdomen, and pelvis, while the appendicular part
consists of the upper and lower extremities. The upper extremities, or limbs, include the
shoulders, upper arms, forearms, wrists, and hands, while the lower extremities include
the hips, thighs, lower legs, ankles, and feet. The abdominal region can be further divided
into nine regions or four quadrants.
The cavities of the body hold the internal organs. The major cavities are the dorsal and
ventral body cavities, while smaller ones include the nasal, oral, orbital (eye), tympanic
(middle ear), and synovial (movable joint) cavities. The dorsal body cavity includes the