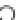Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
The Thevenin's equivalent circuit is shown in the following figure.
Outside
I
Na-K
R
TH
R
Cl
I
Cl
V
m
I
V
TH
E
Cl
Inside
E
Cl
¼
V
TH
according to Table 12.2, no current flows. This is the actual situation in most
nerve cells. The membrane potential is determined by the relative conductances and Nernst
potentials for
Since
K
þ
and
Na
þ
. The Nernst potentials are maintained by the
Na-K
active pump that
Cl
is usually passively distributed across the membrane.
maintains the concentration gradient.
The Na-K Pump
As shown in Example Problem 12.4 and Section 12.4, there is a steady flow of
K
þ
ions out
Na
þ
ions into the cell even when the membrane is at the resting potential.
Left unchecked, this would drive
of the cell and
E
K
and
E
Na
toward 0. To prevent this, current generators
depicting the
pump are used that are equal to and the opposite of the passive currents
and incorporated into the model, as shown in Figure 12.14.
Na-K
12.5.2 Capacitive Properties
Capacitance occurs whenever electrical conductors are separated by an insulating
material. In the neuron, the cytoplasm and extracellular fluid are the electrical conductors,
Outside
I
Na
R
Na
R
K
I
K
R
Cl
I
Na
I
K
V
m
-
-
-
E
Na
E
K
E
Cl
+
+
+
Inside
FIGURE 12.14
Circuit model of the three passive channels for a small area of the nerve at rest with each ion
channel represented by a resistor in series with a battery. The
Na-K
active pump is modeled as two current sources
within the shaded box.