Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
+60
−
60
2
4
6
8
10
Time (ms)
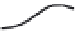
FIGURE 12.4
An action potential.
12.3.2 Resting Potential, Ionic Concentrations, and Channels
A resting membrane potential exists across the cell membrane because of the
differen-
tial distribution
of ions in and around the membrane of the nerve cell. The cell maintains
these ion concentrations by using a selectively permeable membrane and, as described
later, an active ion pump. A selectively permeable cell membrane with ion channels is
illustrated in Figure 12.2. The neuron cell membrane is approximately 10 nm thick, and
because it consists of a lipid bilayer (i.e., two plates separated by an insulator), it has
capacitive properties. The extracellular fluid is composed of primarily
Na
þ
and
Cl
,
K
þ
and
A
.Thelarge
and the intracellular fluid (cytosol) is composed of primarily
A
) are primarily amino acids and proteins that do not cross the mem-
brane. Almost without exception, ions cannot pass through the cell membrane except
through a channel.
Channels allow ions to pass through the membrane, are selective, and are either
passive or active. Passive channels are always open and are ion specific. Figure 12.5
illustrates a cross section of a cell membrane with passive channels only. As shown, a
particular channel allows only one ion type to pass through the membrane and prevents
all other ions from crossing the membrane through that channel. Passive channels exist
for
organic anions (
Ca
þ2
, which is important
in the excitation of the membrane at the synapse, as described in Section 12.8.Active
channels, or gates, are either opened or closed in response to an external electrical or
chemical stimulation. The active channels are also selective and allow only specific ions
to pass through the membrane. Typically, active gates open in response to neurotransmit-
ters and an appropriate change in membrane potential. Figure 12.6 illustrates the concept
of an active channel. Here,
Cl
,
K
þ
,and
Na
þ
. In addition, a passive channel exists for
Cl
passes through a
passive channel. As will be shown, passive channels are responsible for the resting mem-
brane potential, and active channels are responsible for the graded response and action
potentials.
K
þ
passes through an active channel and