Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ANNs consist of multiple interconnected neurons. Different types of neurons can be
represented in an ANN. Neurons are arranged in a layer, and the different layers of neu-
rons are connected to other neurons and layers. The manner in which the neurons are
interconnected determines the architecture of the ANN. There are many different ANN
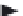
architectures, some of which are best suited for specific applications. Figure 11.39 shows
a schematic of a simple ANN with three layers of neurons and a total of six neurons. The
first layer is called the
and has two neurons, which accept the input to the net-
work. The middle layer contains three neurons and is where much of the processing occurs.
The
input layer
has one neuron that provides the result of the ANN.
Mathematical equations are used to describe the connections between the neurons.
The diagram in Figure 11.40 represents a single neuron and a mathematical method for
determining the output of the neuron. The equation for calculating the total input to the
neuron is
output layer
x
¼ð
Input
1
Weight
1
Þþð
Input
2
Weight
2
Þþ
Bias Weight
ð
11
:
59
Þ
Output
Layer
Input
Layer
Hidden
Layer
FIGURE 11.39
A simple artificial neural network (ANN) with six neurons and three layers.
Neuron
Weight
1
Input 1
x
Σ
y = Output of Neuron
g(x)
Weight
2
Input 2
Bias
FIGURE 11.40
A single neuron showing mathematical input and output relationships.