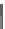Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1.0
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
25
(a)
Age (years)
1.0
0.5
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
25
(b)
Age (years)
FIGURE 11.37
(a) Crisp sets for the classification of people by age. (b) Fuzzy sets for the classification of people
by age.
fuzzy union operator, and Figure 11.38c shows the negation operator for fuzzy sets. The
solid line indicates the result of the operator in each figure.
Although it is easy to form fuzzy sets for a simple example such as age classification, fuzzy
sets for more sophisticated applications are derived by using sophisticated calibration techni-
ques. The linguistic variables are formulated mathematically and then can be processed by
computers. Once the fuzzy sets have been established, rules are constructed. Fuzzy logic is
a rule-based logic. Fuzzy systems are constructed by using a large number of rules. Most
rules used in fuzzy logic computing are if-then statements that use linguistic variables.
Two simple rules that use the fuzzy sets for age classification might be the following:
If the patient is YOUNG, then use TREATMENT A.
If the patient is MIDDLE-AGED or OLD, then use TREATMENT B.
The degree of membership in a group helps to determine which rule will be used and,
consequently, the type of action that will be taken or, in the preceding example, the sort
of treatment that will be used. Defuzzification methods are used to determine which rules
will be used to produce the final output of the fuzzy system.
For many applications, fuzzy logic has significant advantages over traditional numeric
computing methods. Fuzzy logic is particularly useful when information is too limited or
too complex to allow for numeric precision, since it tolerates imprecision. If an accurate
mathematical model cannot be constructed, fuzzy logic may prove valuable. However, if