Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CASE STUDY: NEONATAL INTENSIVE CARE UNIT (NICU)
Throughout time, low birth weight, oftentimes arising from premature birth, has been a major
factor affecting infant survival. Underweight infants, who are typically classified as either low
birth weight (LBW) (less than 1,500 g) or very low birth weight (VLBW) (less than 1,000 g), must
be treated with the utmost caution and care in order to maximize their chances of survival.
Advances in premature-infant medical care, such as improved thermoregulation and ventilation
techniques, have greatly decreased the mortality rate among LBW and VLBW infants. Included in
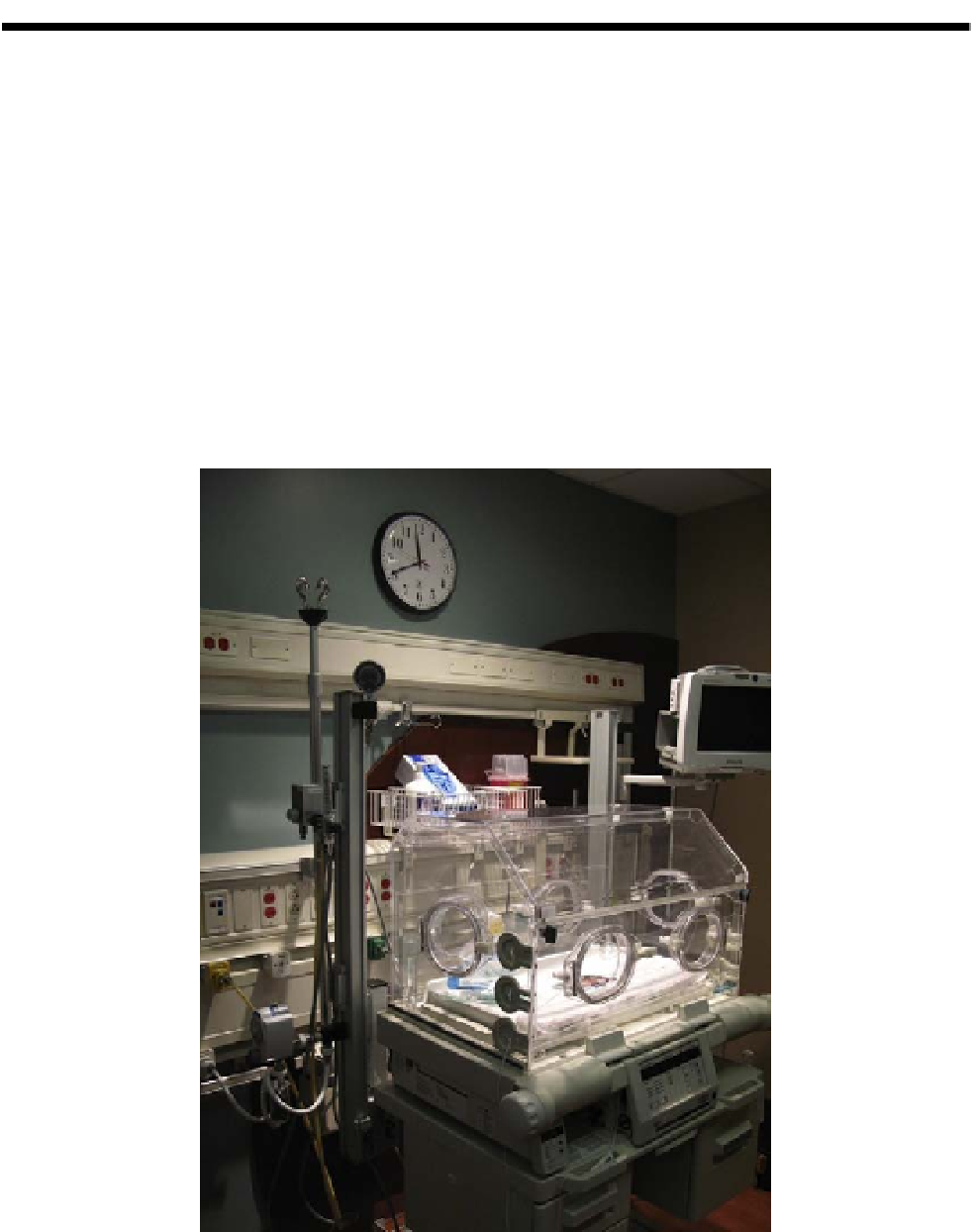
these advances was the creation of the NICU (Figure 2.2), where all the necessary equipment
needed to sustain the life of the child could be kept conveniently in close proximity to one another.
One of the most important devices used in the NICU is the incubator. This device, typically
molded of see-through plastic, is used to stabilize the body temperature of the infant. In essence,
the incubator allows the medical staff to keep the newborn warm without having to wrap it in
FIGURE 2.2
A Neonatal Intensive Care Unit.
Courtesy of http://www.pediatrics.ucsd.edu/Divisions/Neonatology/
Pictures/Image%20Library/NICU%20Bed.jpg.