Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
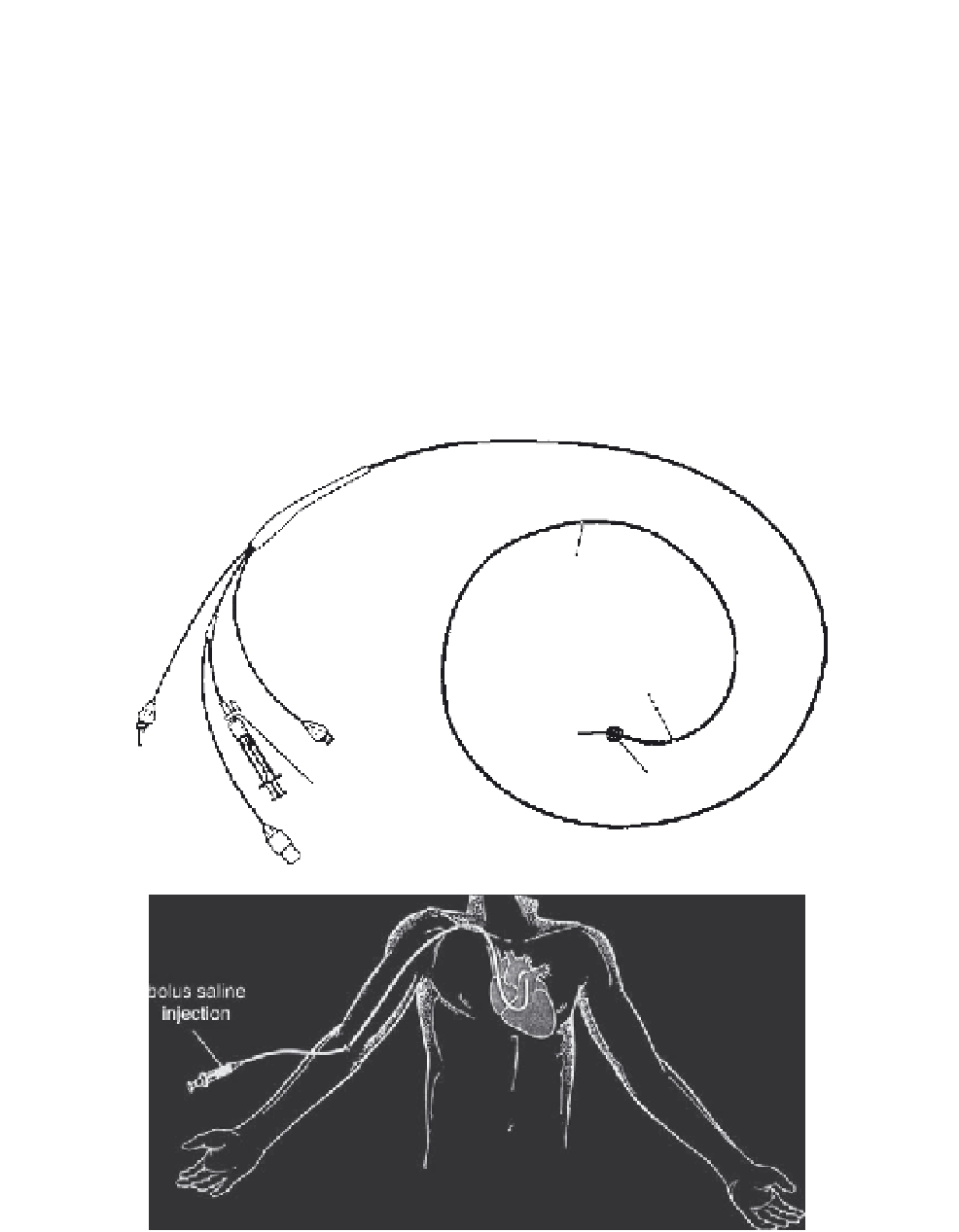
A thermistor sensor can be employed in a Swan-Ganz thermodilution technique for mea-
suring cardiac output (the volume of blood ejected by the heart each minute) and assessing
ventricular function. The procedure is normally performed in the operating room or the
intensive care unit. It involves a rapid bolus injection of a cold indicator solution, usually
3-5 ml of a sterile saline or dextrose solution kept at 0
C, into the right atrium via a flexible
pulmonary artery catheter (Figure 10.22).
The 5 or 7 French-size thermodilution catheter contains a small balloon and is normally
inserted into either the femoral or internal jugular veins. The catheter is constructed of a
radiopaque material to enable easy visualization by an x-ray machine. It contains three
ports: a balloon inflation port to guide the flexible tip to the right location, a proximal cen-
tral venous port, and a distal pulmonary artery port. After the balloon is inflated, the tip of
the flexible catheter is passed across the tricuspid valve through the right ventricle, across
the pulmonary valve, and into the pulmonary artery. The proximal and distal ports can
Proximal
(right atrial)
side hole
Thermistor
Distal
end hole
Distal
port
Balloon
inflation port
Proximal
port
Balloon
Thermistor
connector
FIGURE 10.22
A Swan-Ganz thermodilution catheter.