Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
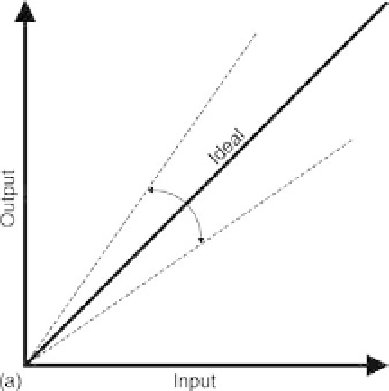
FIGURE 10.2
Changes in input versus output response caused by (a) sensitivity errors and (b) offset errors.
and sensitivity drifts specify the total error due to drift. Knowing the values of these drifts can
help to compensate and correct sensor readings.
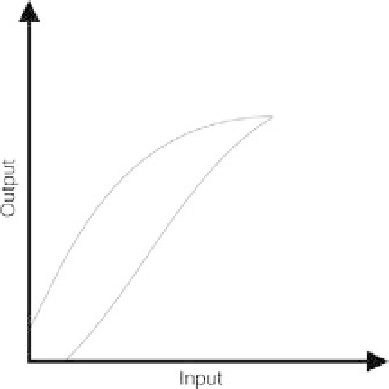
Hysteresis
In some sensors, the input-output characteristic follows a different nonlinear trend,
depending on whether the input quantity increases or decreases, as illustrated in Figure 10.3.
For example, a certain pressure gauge may produce a different output voltage when the input
pressure varies from zero to full scale and then back to zero. When the measurement is not
perfectly reversible, the sensor is said to exhibit
. If a sensor exhibits hysteresis, the
input-output relation is not unique but depends on the direction change in the input quantity.
The following sections will examine the operation principles of different types of bio-
medical sensors, including examples of invasive and noninvasive sensors for measuring
biopotentials and other physical and biochemical variables encountered in different clinical
and research applications.
hysteresis
FIGURE 10.3
Input versus output response of a sensor with hysteresis.