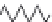Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
+
+
V
S
V
S
I
S
−
−
(a) (b) (c)
FIGURE 9.10
Basic symbols used for independent sources: (a) battery and (b) ideal voltage source. V
s
can be a
constant DC source (battery) or a time-varying source. (c) Ideal current source I
s
.
+
-
V
S
I
S
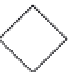
FIGURE 9.11
Basic symbols used for dependent or controlled sources. (Left) Controlled voltage source. The
voltage
v
s
is a known function of some other voltage or current in the circuit. (Right) Controlled current source.
The current
i
s
is a known function of some other voltage or current in the circuit.
cannot be determined without knowledge of the rest of the circuit. Independent sources are
devices for which the voltage or current is given and the device maintains its value regard-
less of the rest of the circuit. A device that generates a prescribed voltage at its terminals,
regardless of the current flow, is called an ideal voltage source. Figures 9.10a and b show
the general symbols for an ideal voltage source. Figure 9.10c shows an ideal current source
that delivers a prescribed current to the attached circuit. The voltage generated by an ideal
current source depends on the elements in the rest of the circuit.
Figure 9.11 shows a dependent voltage and current source. A dependent source takes on
a value equaling a known function of some other voltage or current value in the circuit. We
use a diamond-shaped symbol to represent a dependent source. Often, a dependent source
is called a controlled source. The current generated for a dependent voltage source and the
voltage for a dependent current source depend on circuit elements in the rest of the circuit.
Dependent sources are very important in electronics. Later in this chapter, we will see that
the operational amplifier uses a controlled voltage source for its operation.
9.4 RESISTANCE
9.4.1 Resistors
A resistor is a circuit element that limits the flow of current through it and is denoted
with the symbol . Resistors are made of different materials, and their ability to impede
current is given with a value of resistance, denoted
R.
Resistance is measured in ohms (
O
),
where 1
1 V/A. A theoretical bare wire that connects circuit elements together has a
resistance of zero. A gap between circuit elements has a resistance of infinity. An ideal resis-
tor follows Ohm's law
,
which describes a linear relationship between voltage and current,
with a slope equal to the resistance.
O ¼