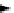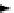Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
7.8.2 Catenary Multicompartment Model
A catenary n-compartment model is shown in Figure 7.27, which is characterized by a
chain of compartments, with each compartment exchanging solute with the two adjacent
compartments, except for the first and last in the chain. Each compartment can have an
input and an output to the environment.
The matrix
A
, given in Eq. (7.106), has nonzero elements defined as
a
¼ð
K
þ
K
Þ
11
10
12
a
i
,
i
1
¼
K
i
1
,
i
,
2
i
n
,
a
ii
¼
K
i
0
þ
K
i
,
ð
i
1Þ
þ
K
i
,
ð
i
þ1Þ
2
i
n
1
ð
7
:
109
Þ
¼
K
i
þ1
,
i
,
2
i
n
1
a
i
,
i
þ1
a
nn
¼
K
n
0
þ
K
n
,
ð
n
1Þ
This system only has real roots.
7.8.3 Unilateral Multicompartment Model
A unilateral n-compartment model is shown in Figure 7.28, which is characterized by a
closed loop of connected compartments, whereby solute circulates around the loop in one
direction only. Each compartment can have an input and an output to the environment.
f
1
(t)
f
2
(t)
f
3
(t)
f
n
(t)
K
n
,n-1
K
32
K
43
K
21
q
1
q
2
q
3
q
n
K
23
K
n-1,n
K
12
K
34
K
10
K
20
K
30
K
n0
FIGURE 7.27
A catenary n-compartment model.
f
1
(t)
f
2
(t)
f
n-1
(t)
K
10
K
12
K
23
K
n-2,n-
1
K
n-1,0
q
1
q
2
q
n-1
K
20
K
n1
K
n-1,n
f
n-1
(t)
q
n
K
n0
FIGURE 7.28
A unilateral n-compartment model.