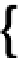Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Extracellular
+
Outside
Lipid
Bilayer
Inside
-
Channel
Intracellular
FIGURE 7.3
A typical cell membrane.
prevents other ions from passing through this channel. Passive channels are always open
and driven by the concentration gradient.
4
Another type of channel is an active channel that
uses energy from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to move ions across the membrane against
a concentration gradient. An active channel may be open all the time, or it may be open or
closed based on the voltage across the membrane.
A third type of channel is called a pump, which exchanges ions from the inside to the
outside using ATP. The neuron cell membrane uses an
Na
þ
K
þ
pump to remove
Na
þ
from
K
þ
from the outside, as discussed in Sections 7.3.4 and
8.4.4. One of the most important functions of the pump is to control cell volume. If cell
volume is not controlled, the cell will swell and burst. Approximately 60 percent of a
neuron's energy requirements are used to maintain the
inside the cell and replaces it with
Na
þ
K
þ
pump.
The use of passive and active channels allows the concentration of ions to be different
inside and outside the cell. Table 7.2 gives approximate concentrations across a mammalian
cell membrane for some important positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged
ions (anions) in moles/liter.
5
The intracellular space (cytoplasm) has organelles with
different ionic compositions. We will return to diffusion across the cell membrane in
Section 7.3.4.
Another example of a membrane is the capillary wall. A capillary wall consists of endo-
thelial cells that separate the interstitial volume from the blood volume. The typical length
of a capillary is approximately 1 mm, with a diameter of 7 mm. Since the diameter of a
4
Or an electric gradient as described in Chapter 12.
5
A mole equals 6
10
23
(Avogadro's number) particles and is defined as a unit in SI. The unit for the
mole is M. For any ion or molecule, a mole's weight equals its atomic weight. So one mole of
:
02
H
O
molecules
2
Cl
¼
4
m
L
Cl
ions
weighs 18 g. Assuming a cell's volume is 1 nL with concentration of
, the number of
inside the cell equals
0
004
M
10
23
molecules
M
10
9
L
10
12
molecules
:
L
6
:
02
1
¼
2
:
408