Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
TABLE 6.10
Cells That Contribute to the Tissue Microenvironment—Cont'd
Transient cells: cells that migrate into a tissue for host defense either prior to or following an inflammatory
stimulus
B lymphocytes/plasma cells
Cytotoxic T cells and natural killer (NK) cells
Granulocytes
Parenchymal cells: cells that occupy most of the tissue volume, express functions that are definitive for the tissue,
and interact with all other cell types to facilitate the expression of differentiated function
Mesenchymal cells (such as fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells) are present in all
tissues. These cells are of connective tissue type.
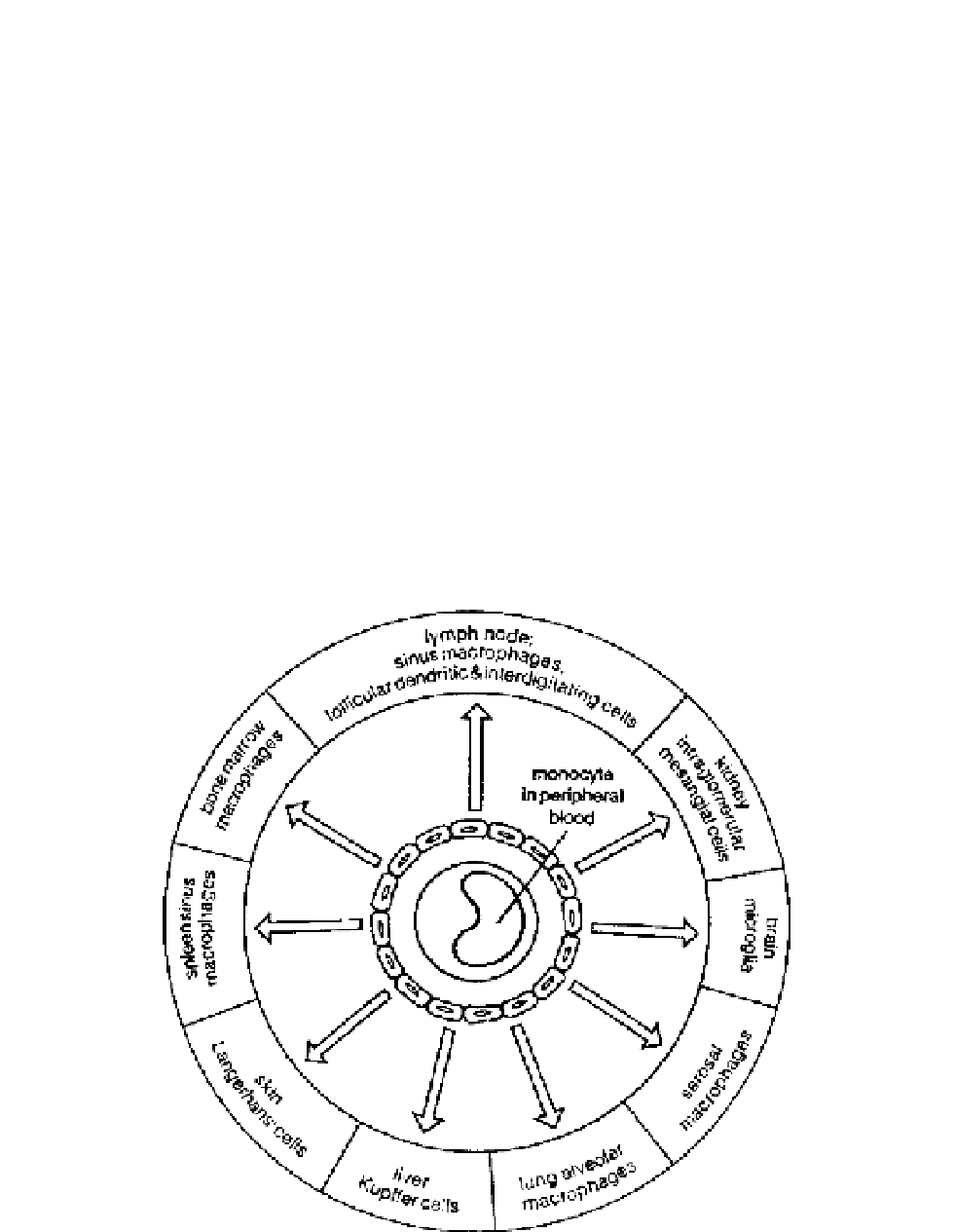
Monocytes are present in all tissues and can take on a variety of different morphologies
(see Figure 6.27). Monocytes can differentiate into macrophages that, once activated,
produce a variety of cyto- and chemokines that influence the behavior of neighboring
cells.
FIGURE 6.27
Distribution of macrophages and their presence in different tissues.
From [6].