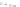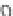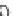Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
INTERATRIAL TRACTS
SINOATRIAL NODE
LEFT BUNDLE
BRANCH
INTERNODAL TRACTS
ATRIOVENTRICULAR
NODE
PURKINJE
FIBERS
BUNDLE OF HIS
RIGHT BUNDLE
BRANCH
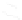
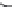
FIGURE 3.20
Pacemaker cells in the sinoatrial node (SA node) depolarize first and send an activation wave-
front through the atria. The propagating action potential slows down as it passes through the atrioventricular node
(AV node), then moves through the bundle of His and Purkinje system very rapidly until it reaches the cells of the
ventricles.
reverses and then becomes reestablished is called an action potential. The cells in the sino-
atrial node depolarize on the average of every 0.83 s in a typical adult at rest. This gives a
resting heart rate of 72 beats per minute, with about
5
/
8
of each beat spent in diastole and
3
/
8
in systole.
Cardiac cells are linked and tightly coupled so action potentials spread from one cell to
the next. Activation wavefronts move across the atria at a rate of about 1 m/s. When cardiac
cells depolarize, they also contract. The contraction process in the atria (atrial systole)
moves blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle and from the left atrium to the
left ventricle (Figure 3.21). The activation wavefront then moves to the atrioventricular
(a)
(b)
FIGURE 3.21
(a) During the first part of the cardiac cycle, the atria contract (atrial systole) and move blood into
the ventricles. (b) During the second part of the cardiac cycle, the atria relax (diastole), and the ventricles contract
(ventricular systole) and move blood to the lungs (pulmonary circulation) and to the rest of the body (systemic
circulation).