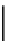Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
mean free path (mfp') below the tissue surface and one negative image source above the tis-
sue surface. The positive source represents a single scatter source in the tissue, and the
height in
of the image source depends on the boundary condition. The transport mean
free path is defined as
z
mfp
0
¼
m
s
Þ
1
=ð
m
a
þ
ð
17
:
44
Þ
With oblique incidence, the buried source should be located at the same path length into
the tissue, with this distance now measured along the new optical path as determined by
Snell's law. It is assumed that (a) the angle of incidence and (b) the indexes of refraction
for both the tissue and the medium through which the light is delivered are known. The
net result is a change in the positions of the point sources, particularly a shift in the
x
direc-
tion. These two cases are shown in Figures 17.8a and b.
N
eg
a
ti
ve
s
o
u
rc
e
3D+2AD
ρ
1
Light
r
2AD
Air
Tissue
x
z
y
3D
ρ
2
Positive source
(a)
θ
t
=
a
rc
si
n
[(
n
i
/
n
t
)s
in
θ
i
]
N
eg
a
ti
ve
source
3D cos
θ
t
+2AD
Δ
x
Light
ρ
1
θ
i
r
2AD
Air
Tissue
y
x
z
3D cos
θ
t
ρ
2
θ
t
Positive
source
3D
(b)
FIGURE 17.8
(a) Positions of point sources in diffusion theory model for normal incidence. (b) Positions of
point sources in diffusion theory model for oblique incidence. The
r
2
are the
distances from the positive and negative point sources to the point of interest on the tissue surface, at a radius
of
y
-axis points out of the page.
r
1
and
r
from the axis of the sources.
y
t
is determined from Snell's law.