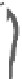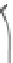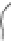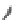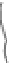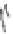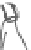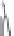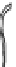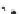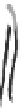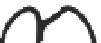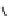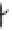Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
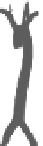
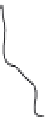
INTERNAL
JUGULAR
VEINS
RIGHT
SUBCLAVIAN
VEIN
SUPERIOR VENA
CAVA
COMMON
CAROTID
ARTERIES
LEFT
SUBCLAVIAN
ARTERY
LEFT
SUBCLAVIAN
VEIN
RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN
ARTERY
ASCENDING
AORTA
DESCENDING
AORTA
COMMON
ILIAC
ARTERIES
INFERIOR
VENA
CAVA
COMMON
ILIAC
VEINS
HEART
(a)
(b)
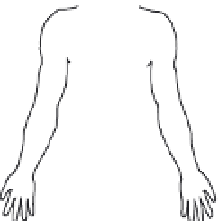
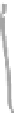
FIGURE 3.17
(a) The distribution of the main arteries in the body that carry blood away from the heart. (b) The
distribution of the main veins in the body that return the blood to the heart.
enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which catalyzes the reversible formation of carbonic acid from
carbon dioxide and water. The primary function of lukocytes is to endow the human body
with the ability to identify and dispose of foreign substances (such as infectious organisms)
that do not belong there—agranulocytes (lymphocytes and monocytes) essentially doing
the “identifying” and granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, and esinophils) essentially
doing the “disposing.” The primary function of platelets is to participate in the blood-
clotting process.
Removal of all hematocytes from blood centrifugation or other separating techniques
leaves behind the aqueous (91 percent water by weight, 94.8 percent water by volume),
saline (0.15N) suspending medium called
plasma
—which has an average mass density of
/- 0.005 g/cm
3
and a viscosity 1½ to 2 times that of water. Some 6.5 to 8 percent
by weight of plasma consists of the plasma proteins, of which there are three major
types—albumin, the globulins, and fibrinogen—and several of lesser prominence.
The primary functions of albumin are to help maintain the osmotic (oncotic) transmural
pressure differential that ensures proper mass exchange between blood and interstitial fluid
at the capillary level and to serve as a transport carrier molecule for several hormones and
other small biochemical constituents (such as some metal ions). The primary function of
the globulin class of proteins is to act as transport carrier molecules (mostly of the
1.035
þ
)
for large biochemical substances, such as fats (lipoproteins) and certain carbohydrates
(muco- and glycoproteins) and heavy metals (mineraloproteins), and to work together with
leukocytes in the body's immune system. The latter function is primarily the responsibility
a
and
b