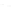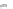Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
ROUGHER
VESICLE
OUTER COMPARTMENT
INNER
COMPARTMENT
RIBOSOME
SMOOTHER
VESICLE
(a)
(b)
(c)
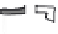
FIGURE 3.9
Subcellular organelles. The endoplasmic reticulum (a), the Golgi apparatus (b), and vesicles
(b) make up the cytomembrane system in the cell. The small circles on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) represent
ribosomes. The area containing ribosomes is called the rough ER, while the area that lacks ribosomes is called
the smooth ER. The mitochondria (c) have a double membrane system that divides the interior into two compart-
ments that contain different concentrations of enzymes, substrates, and hydrogen ions (H
þ
). Electrical and chemical
gradients between the inner and outer compartments provide the energy needed to generate ATP.
The mitochondria (Figures 3.9c and 3.10) contain two membranes: an outer membrane that
surrounds the organelle and an inner membrane that divides the organelle's interior into
two compartments. Approximately 95 percent of the ATP required by the cell is produced
in the mitochondria in a series of oxygen-requiring reactions that produce carbon dioxide
as a by-product. Mitochondria are different from most other organelles in that they contain
their own DNA. The majority of the mitochondria in sexually reproducing organisms, such
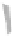
FIGURE 3.10
Scanning electron micrograph of a normal mouse liver at 8,000X magnification. The large round
organelle on the left is the nucleus. The smaller round and oblong organelles are mitochondria that have been sliced
at different angles. The narrow membranes in parallel rows are endoplasmic reticula. The small black dots on the ERs
are ribosomes.
Photo courtesy of Valerie Knowlton, Center for Electron Microscopy, North Carolina State University.