Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Kalman Filter
IMME
MC-IMME
Chest 1
0.8
Chest 2
Chest 3
0.4
0.6
0.6
0.5
0.2
0.4
0.4
0.2
0
0.3
100
200
300
400
100
200
300
400
100
200
300
400
Predicti
o
n Time Horizo
n
(ms)
Prediction Time Horizo
n
(ms)
Predictio
n
Time Horizo
n
(ms)
0.4
0.8
Head 1
Head 2
Head 3
0.8
0.6
0.2
0.7
0.4
0.6
0.2
0
0.5
100
200
300
400
100
200
300
400
100
200
300
400
Prediction Time Horizon(ms)
Prediction Time Horizon(ms)
Prediction Time Horizon(ms)
0.2
Upper Body 1
Upper Body 2
Upper Body 3
0.6
1.2
0.1
0.4
1
0.2
0.8
0
100
200
300
400
100
200
300
400
100
200
300
400
Prediction Time Horizon(ms)
Prediction Time Horizon(ms)
Prediction Time Horizon(ms)
Fig. 3.15
Error performance among prediction time horizon
improvements were less than 7 % with comparison to IMME. The average
improvements were 42.77 % for KF and 16.35 % for IMME.
In the Head_1 dataset, the error performance was significantly improved by
80.24 % for KF and 73.40 % for IMME of the average prediction time horizon.
Notice that the improvement of error performance for the proposed method
maintained around 65 % across the prediction time horizons. In the other Head
motion datasets, the proposed method can improve other methods, even though the
average improvements were less than 5 % in comparison to IMME. The average
improvements were 47.71 % for KF and 27.92 % for IMME.
In the Upper_Body_1 dataset, the proposed method was improved by 68.79 %
for KF and 52.52 % for IMME of the average prediction time horizon. We can
notice that the improvement of MC-IMME maintained around 40 % across the
prediction time horizons. We can also notice that the proposed method outperforms
KF for 44.10 % and IMME for 20.91 % of the average prediction time horizon over
all the datasets, even though the average improvements were less than 6.3 % for
Upper_Body_2 and 3.91 for Upper_Body_3 in comparison to IMME.
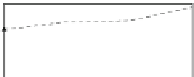
(3) Velocity Estimation
Figure
3.16
shows the average velocity of group number 1 for Head_1 dataset.
The velocity estimations of MC-IMME align more closely to the measurements,
than KF and IMME values. The overall improvements for the group number 1 of
Head_1 dataset are 50.76 % for KF and 49.40 % for IMME.
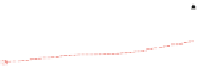
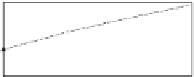
(4) Effect of the Feedback/Forward Method
We would like to show the advantage of the proposed feedback/forward method
by comparing the performance of velocity estimation of MC-IMME with no
feedback/forward vs. feedback/forward. We have evaluated the tracking perfor-
mance of the average velocity for the Chest_3 dataset in Fig.
3.17
. We have























































































































































































































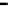




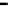

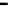

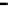


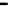
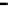
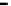
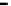

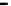

Search WWH ::

Custom Search