Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
that is individually optimized to each patient, (ii) adaptive linear prediction (ALP) as
a benchmark method, and (iii) kernel density estimation-based prediction (KDE)
[
15
] that is a statistical method to estimate the joint probability distribution of the
covariate and response variable using kernel density approximation. The NRMSE
using (i) O-ANN was applied to the patient breathing data of the CyberKnife
treatment facility at Georgetown University, and (ii) ALP and (iii) KDE were
applied to patient data acquired with real-time position management, called the
RPM system by Varian Medical, Palo Alto, CA. The error performance for these
studies can be improved from the standard RNN; the proposed CNN 47.21 % (the
best
improvement),
O-ANN
25.27 %,
ALP
23.79 %
and
KDE
33.83 %,
respectively.
5.4.5 Prediction Overshoot Analysis
We would like to evaluate the prediction accuracy with evaluation criteria using
the marginal value (c) (52) in
Sect. 4.3.4
.
We add and subtract the marginal value
from the measurement values, so that we can get the upper and lower bounds for
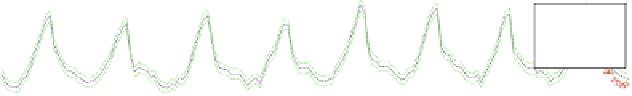
each patient; for example, Patient DB35 and DB88 shown in Fig.
5.7
.
Figure
5.7
shows the prediction overshoots of regular motion (DB35 in Class 1)
and irregular motion (DB88 in Class 5). In the regular breathing patterns of
Fig.
5.7
a, the proposed CNN has no prediction overshoot, whereas the overshoot
percentage of RNN is more than 40 %. In the irregular breathing pattern of
(a)
CNN
RNN
Measurement
Upper Bound
Lower Bound
0
-0.2
-0.4
-0.6
2.906
2.9065
2.907
2.9075
2.908
2.9085
2.909
x 10
4
(b)
Data Time Index (Second)
0.4
CNN
RNN
Measurement
Upper Bound
Lower Bound
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
-0.1
-0.2
3.37
3.3705
3.371
3.3715
3.372
3.3725
3.373
x 10
4
Data Time Index (Second)
Fig. 5.7 Prediction overshoot comparison. (a) Patient DB35 of class 1 (time index:
2.906 9 104 * 2.909 9 104), and patient DB88 of Class 5 (time index: 3.37 9 104
* 3.373 9 104) with the sampling rate of 5 Hz. The RNN presents more prediction overshoots
in comparison to CNN. The proposed CNN has no prediction overshoot, whereas the overshoot
percentage of RNN is more than 50 % in the regular breathing pattern (a). In the irregular breathing
pattern (b), the overshoot percentages of CNN and RNN are 23 % and 46 %, respectively, in this
particular time index


















































































































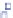














































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search