Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
100
60
80
60
30
40
0
0
3
6
9
12
15
20
CA125 concentration/U mL
1
0
0
10
20
30
40
CA125 concentration/U mL
1
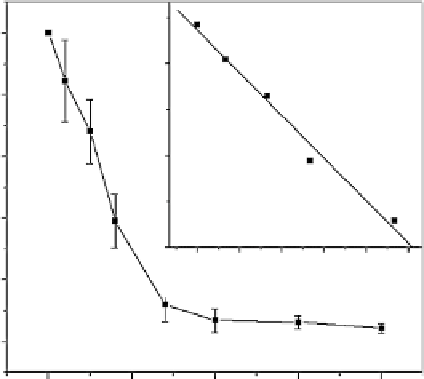
FIGURE 16.10
Calibration for CA125 determination. Inset: plot of the decrease in DPV peak current vs
CA125 concentration (adapted from [138]).
fabrication reproducibility. These kinds of reagentless immunosensors are highly use-
ful for medical applications, because the use of fewer reagents in clinical assays leads
to less interference and more accuracy, especially in real samples such as serum, urine,
and other biological fl uids.
16.3.4 Immunoaffi nity columns
The sol-gel-entrapped Abs have also been employed in affi nity purifi cation by packing
into column (immunosorbent). The successful entrapment of dopants requires substan-
tial screening of the sol-gel preparation procedure parameters, including examination of
the effects of sol-gel format and composition on binding [40, 63]. Altstein
et al.
[140]
immobilized TNT IgG antibodies in TMOS monoliths. The resulting wet gels were
thoroughly crushed and packed into columns for the separation and quantifi cation of
TNT. Lira
et al.
[141] reported 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) immunosorbent
for the extraction of 2,4-D ester. The immunosorbent showed good precision, no leak-
age of the antibody, and a binding capacity of 130 ng of 2,4-D ester per mg of immobi-
lized antibody, corresponding to 42% of the free antibody activity. Similarly Bronshtein
et al.
[20] reported an immunosorbent column for atrazine using monoclonal antibodies
without purifi cation. These promising results illustrated that sol-gel entrapped antibod-
ies could be effi ciently employed in affi nity separation and online detection.





Search WWH ::

Custom Search