Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
(a)
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
(b)
(c)
(i) (ii) (iii)(iv) (v) (vi)
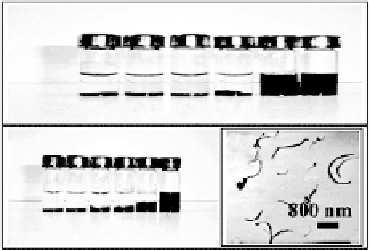
FIGURE 15.10
Photographs of vials containing 0.5 mg mL
1
of SWCNT (a) and MWCNT (b) in differ-
ent solutions: phosphate buffer (0.05 M, pH 7.4) (i), 98% ethanol (ii), 10% ethanol in phosphate buffer (iii),
0.1% Nafi on in phosphate buffer (iv), 0.5% Nafi on in phosphate buffer (v), and 5% Nafi on in ethanol (vi).
Also shown (c) is a TEM image of a 0.5% Nafi on solution containing 0.3 mg mL
1
of MWCNT. (Reprinted
with permission from [64]. Copyright (2003) American Chemical Society.)
stirring conditions at 70ºC for 30 min. After fi ltering and washing again on a 100 nm
pore fi lter, the cut nanotubes are suspended at a density of 0.1 mg ml
1
in water with
the aid of 0.5% weight Triton X-100 surfactant. Such an acid treatment shortens the
CNTs and functionizes CNTs with carboxylic acid groups. Cyclic voltammetry shows
well-behaved peak currents for the redox reaction of the carboxylic acid group at a
CNT-modifi ed GC electrode in buffer solutions [35].
The oxidative procedure of CNTs alone may generate a stable CNT suspension
which can be used for the preparation of CNT coated electrodes. Other procedures to
prepare CNT suspensions are based on non-covalent stabilization of CNTs by using
either surfactants or polymers. An excellent review on this subject has been published
[61]. For the preparation of polymer-assisted CNT suspensions, a simple procedure
for dispersing CNTs in aqueous solutions with a natural polymer gum arabic has
been described [63]. Due to the physical adsorption of the polymer, a stable disper-
sion of full-length, well-separated, individual CNTs is formed in water. Wang
et al.
have demonstrated the ability of a perfl uorosulfonated polymer Nafi on to solubilize
CNTs in water (see Fig. 15.10). The CNT coated electrodes formed with this suspen-
sion dramatically enhanced the redox activity of hydrogen peroxide at CNT/Nafi on
coated electrodes and helped to prepare oxidase-based amperometric biosensors [64].
Zhang
et al.
have solubilized CNTs in aqueous solution of a biopolymer chitosan
(CHIT) which was used to modify electrodes for the development of sensors and bio-
sensors [65]. Such a CNT/CHIT dispersion can easily attach the redox mediators such
as toluidine blue [66] and azure dye [67] to form composite fi lms that facilitate the
electrooxidation of NADH that can be applied to a large group of NAD
-dependent
dehydrogenase enzymes for designing bioelectrochemical devices.
Surfactants are a low cost but effective additive for suspending CNTs in water.
There have been numerous reports regarding the dispersion of CNTs in aqueous solu-
tion with the help of surfactants. It has been demonstrated that various surfactants have
different infl uences on the suspendability of CNTs due to distinct CNT-surfactant





Search WWH ::

Custom Search