Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
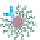
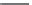
Step 1.
Target Protein
Capture with
MMP Probes
A
B
Step 2.
Sandwich Captured Target
Proteins with NP Probes
1.
SH
Bevine Serum Albumin
2.
3.
Nanoparticle (NP) Probe
Target Protein
(PSA)
13 nm NPs for Bio-Bar-Code PCR
30 nm NPs for PCR-less Method
1.
Step 5.
Chip-Based Detection
of Bar-Code DNA for
Protein Identification
2.
Bevine Serum Albumin
Step 4.
Polymerase
Chain Reaction
Step 3.
MMP Probe Separation
and Bar-Code DNA
Dehybridization
Magnetic Microparticle
(MMP) Probe
Bar-Code DNA
Ag
Au
Gold Nanoparticle
SH Capture DNA
Bar-Code DNA
Amine-Functionalized
Magnetic Particle
Monoclonal Anti-PSA
Polyclonal Anti-PSA
M
Step 4.
PCR-less Detection
of Bar-Code DNA from
30 nm NP Probes
Magnetic
Field
Plate 14
The bio-bar-code assay method. (a) Probe design and preparation. (b) PSA detection and bar-code DNA amplifi cation
and identifi cation (Reproduced from [17] with permission.) (see Figure 14.2).
MB
Biotinylated
Capture Probe
Biotinylated
Target
CdS labeled
probe
Cd
Amplification
HBr
Au(III)
Silver Enhancement
HNO
3
HNO
3
Ag(I)
Zn
Cd
Pb
Au(III)
MD
Me
Au(III)
Me
2
Mercury Coated Glassy
Carbon Electrode
Me
2
M
Au(I)
Disposable Screen-
Printed Electrode
MD
Au(I)
Disposable Screen-
Printed Electrode
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
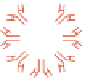
Plate 15
Nanoparticle-based electrochemical detection of DNA. These assays involve the introduction of the probe coated
magnetic beads, the addition of the target/hybridization event, magnetic removal of unwanted materials, binding of the metal, and
amplifi ed electrochemical detection of the dissolved gold (a), silver (b), and cadmium sulfi de (d) nanoparticles. Me: metal tag. Also
shown are solid-state stripping (c) and multi-target (e) detection protocols. See text for details (see Figure 14.3).













































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search