Biomedical Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
CE/RE
WE
PAPP
PAP
O
PAP
R
PAP
R
PAP
O
Enzyme alkaline phosphatase
Antibody anti-goat lgG
Antigen goat lgG
APTES-GA
Glass
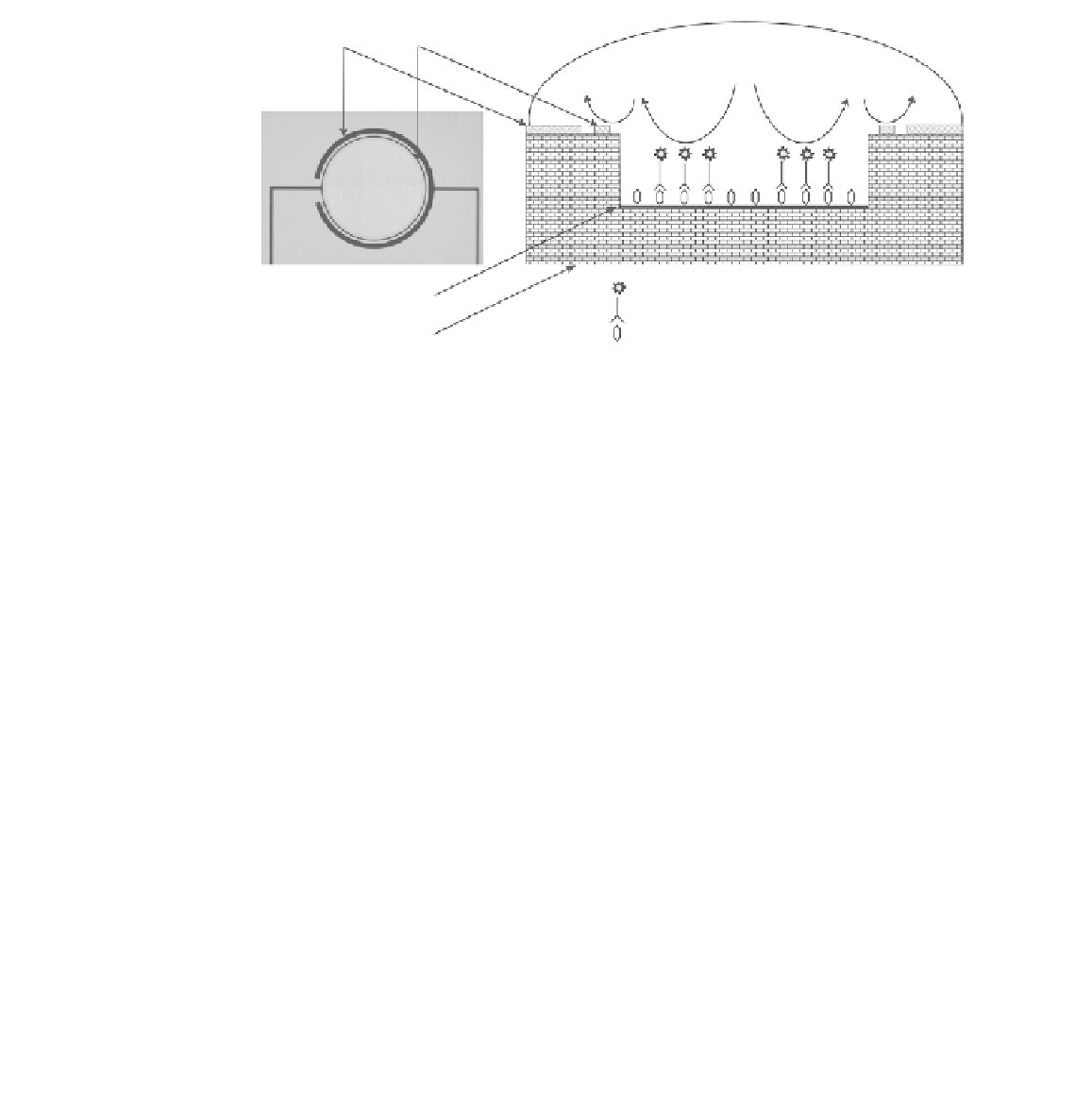
FIGURE 11.31
Schematic of electronic ELISA microchip.
study, Lim
et al.
[124] employed a microfabricated on-chip electrochemical fl ow immu-
noassay for measurements of down to 200 ng ml
1
concentrations of histamine in whole
blood based on ferrocene-labeled IgG. Gabig-Ciminska
et al
. [125] described a silicon-
based chip electric detector coupled to bead-based sandwich hybridization used for the
measurement of 10
10
molecules of 16S rRNA in an
E. coli
RNA extract. Paramagnetic
beads with immobilized capture probes were used and the detection was accomplished
employing redox cycling of generated p-aminophenol on an interdigitated array of
gold microband electrodes in a fl ow system. Microelectrochemical immunoassays for
very small sample volumes can also be realized by the use of antibodies attached to
gold recessed microdisks at the bottom of microcavities. Aguilar
et al
. [126] measured
pg ml
1
levels of mouse IgG by detecting the enzymatic generation of p-aminophenol
on microband electrodes close to the recessed microdisks in the same microcavity.
Based on a large number of such microcavities, the latter concept could be used to
carry out a large number of stimultaneous immunoassays. Dong
et al.
[127] reported
a microchip with novel electrochemical detection architecture as shown in Fig. 11.31
for enzyme immunoassay sensors. The microchip is composed of dual-ring working
and counter electrodes, and a sensing cavity chamber was made on a glass slide. The
glass surface of the microchip was coated by 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES).
Goat IgG, as an example, was covalently captured on APTES-modifi ed glass surfaces
through glutaraldehyde (GA) as a cross-linker. Enzyme substrate, p-aminophenyl phos-
phate (PAPP) was prepared by electrolysis. The enzyme conversion from home-syn-
thetic PAPP to p-aminophenol (PAP) was detected by differential pulse voltammetry
(DPV), demonstrating a good sensitivity of 100 fg/ml.
11.4.3.2 Potentiometry
The most common potentiometry involves an instrument called a “pH-Stat”, in which a
glass (pH) electrode follows reactions that either consume or produce protons. Since pH




Search WWH ::

Custom Search